Major Cyber Attacks that shaped 2023

Reading Time: 5 Minutes
Landscape of Cyber Threats in 2023
As we step into 2024, it is imperative to reflect on the cyber threat landscape of the preceding year, 2023, which witnessed a surge in both the frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks.
Notably, the year marked an escalation in the exploitation of vulnerabilities, with ransomware, phishing, and supply chain attacks emerging as predominant vectors.
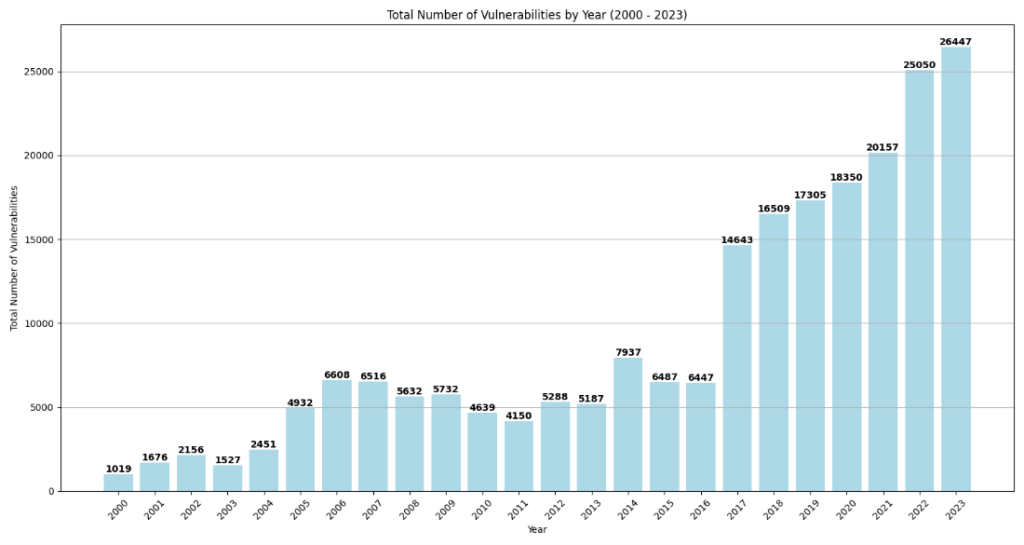
In 2023, 29065 vulnerabilities were disclosed, surpassing the total number of vulnerabilities disclosed in 2022 by more than 4000 CVEs.
Total Number of Vulnerabilities by Year – source: qualys.com
Further examination unveils alarming statistics, including the exploitation of over 7,000 vulnerabilities with proof-of-concept code and a mean time to exploit of 44 days.
In 2023, TA505, also identified as the CL0P Ransomware Gang, emerged as a significant cyber threat. The group orchestrated a high-profile cyberattack, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities across crucial platforms such as MOVEit, GoAnywhere MFT, and more.
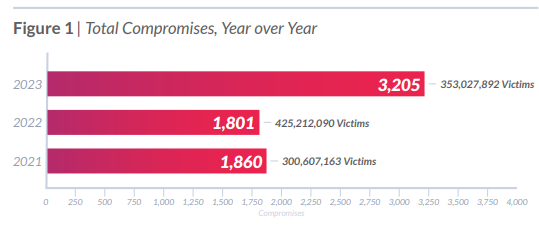
Furthermore, 2023 underscored a significant rise in data breach incidents. With a total of 3205 reported cases, the number of breaches witnessed a substantial increase compared to the 1801 data compromises documented in the Identity Theft Resource Center’s 2022 Data Breach Report. The breaches in 2023 impacted a staggering 8,214,886,660 records, underscoring the growing scale and sophistication of cyber threats, while impacting companies like T-Mobile (twice), MOVEit, Fortra, etc.
Total Compromises Year over Year – source: Identity Theft Resource Center, Annual Data Breach Report 2023
Supply chain attacks also posed risks, with attackers targeting software vendors or cloud services providers to infiltrate their networks and customers. Since 2018, the number of organizations affected by Supply Chain Attacks has gradually increased. However, the impact on organizations has risen sharply by over 2,600%. This surge translates to more than 54 million victims, constituting 15% of the total victims in 2023.

Growing number of Organizations Impacted since 2018 – source: Identity Theft Resource Center, Annual Data Breach Report 2023
Noteworthy Cybersecurity Incidents
Multiple Data Breaches at T-Mobile
The breach, which began around November 25, 2022, went undetected until January 5, 2023, when T-Mobile contained and resolved the incident within a day.
The cause of the breach was unauthorized access through an API. However, T-Mobile didn’t provide specific details about the nature of the API flaw that was exploited or how the unauthorized access occurred through the API.
The compromised data impacting 37 million consumers included customer names, billing information, email addresses, phone numbers, dates of birth, and specific details related to T-Mobile accounts.
T-Mobile also played down the incident, claiming stolen data is commonly found in marketing databases. However, the breach exposed customers to potential phishing and identity fraud risks.
Sensitive details like passwords and financial information remained unaffected, according to T-Mobile. The company insisted there’s no evidence of compromise to its network or systems.
Second data breach in 2023
In September 2023, T-Mobile faced a significant data breach, marked by two distinct incidents. Firstly, employee data, including email addresses and partial Social Security Numbers, surfaced on a hacker forum. This stemmed from a breach at Connectivity Source, a T-Mobile retailer, highlighting potential risks of identity theft due to a third-party service provider’s compromise.
Additionally, a T-Mobile app glitch later exposed payment data for fewer than 100 customers (89GB of data), inadvertently revealing personal details like names, phone numbers, addresses, account balances, and partial credit card information. Though initially reported to impact a small group, concerns were raised about a potential impact on millions. However, T-Mobile has not disclosed the exact number of affected customers.
See Also: The Bug Bounty Hunting Course
A Practical Guide to Hacking Techniques for finding Top Bugs.
3CX Software Double Supply Chain
In the latter part of March 2023, 3CX made public the revelation that its desktop applications, designed for both Windows and macOS, had fallen victim to a supply chain compromise involving malicious code.
The compromise in the software supply chain spread malware through a tampered version of 3CX’s authentic software, which had been made available for download on their official website.
A series of significant vulnerabilities within the widely utilized 3CX VOIP desktop client tool, which had a user base exceeding 600,000 globally, has been pinpointed as CVE-2023-29059. This exploit carries a QDS score of 95 and a CVSS score of 7.8.
The impacted software involved versions preceding 3CX Desktop App 18.12.416. This version included malicious code, initiating a downloader known as SUDDENICON. SUDDENICON subsequently obtained further command and control (C2) servers from encrypted icon files hosted on GitHub.
Upon decryption, the C2 server facilitated the download of a third stage identified as ICONICSTEALER, a data miner specializing in pilfering browser information.
Utilizing this tactic facilitated compromising both Windows and macOS platforms, enabling the extraction of comprehensive system details and the retrieval of stored credentials from multiple browsers.
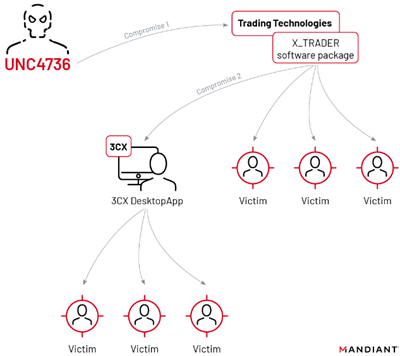
Mandiant monitored and attributed this operation to UNC4736, a cluster of activity suspected to be linked to North Korean actors.
3CX software supply chain compromise linked to Trading Technologies software supply chain compromise –
source: Mandiant
Zero-Day Vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer Exploited for Data Theft
In the recent past, a critical vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer, a secure managed file transfer software, was identified by both Progress and Mandiant.
Between May 31st and June 2nd, 2023, a critical vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer, a secure managed file transfer software, was identified by both Progress and Mandiant.
Progress, in its advisory, disclosed that the vulnerability, present in MOVEit Transfer versions before 2021.0.6 (13.0.6) up to 2023.0.1 (15.0.1), exposed an SQL injection risk in the web application. This flaw could potentially have led to escalated privileges and unauthorized access to the MOVEit Transfer database.
The exploitation of this vulnerability occurred in the wild during May and June 2023 and could have been carried out through both HTTP and HTTPS.
Mandiant’s observations shed light on the real-world consequences of this vulnerability. The exploitation of the zero-day vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-34362, was widespread, leading to data theft incidents ranging from government institutions to public and private organizations. Targets included BBC, the public school system of New York City, British Airways, along with various others.
As per the ongoing count provided by Emsisoft, upwards of 2,000 organizations have documented falling victim to attacks, resulting in data breaches impacting over 62 million individuals. The predominant focus of these attacks has been on entities based in the United States.
Mandiant’s incident response engagements revealed that malicious actors were quick to deploy web shells and initiate data theft, with some instances occurring within minutes of exploitation.
The campaign, initially seemingly opportunistic, took a more sinister turn on June 6, 2023, when a post on the CL0P^_-LEAKS data leak site claimed responsibility for the activity. The threat actors behind this campaign initially attributed to UNC4857 and later merged into FIN11 by Mandiant, operated with a focus on extortion. They then demanded an extortion fee from victims under the threat of posting stolen data on the data leak site.
Figure 2: CL0P^_- LEAKS DLS post, source: mandiant.com
The campaign’s impact extended beyond the directly observed organizations in Canada, India, and the U.S., indicating a broader reach and potential consequences across various industries.
The incident related to MOVEit underscores the scale and significance of supply chain attacks in 2023.To illustrate, ITRC reported that threat actors exploiting a MOVEit product directly affected 102 entities. Yet, the repercussions extended indirectly to 1,271 organizations when data stored in or accessed by a MOVEit product or service was compromised through a vendor or vendors.
Numerous legal actions have ensued in the aftermath of these incidents. The repercussions of the MOVEit breach and other notable cyber-attacks prompted the SEC to mandate that public companies make disclosures within four days of identifying a cybersecurity incident, with exceptions made for situations where disclosure might pose a risk to national security or public safety.
See Also: Recon Tool: fetchmeurls
Casino Operator Attacks
MGM Resorts faced a disruptive cyberattack in September 2023, affecting operations across iconic Las Vegas properties like the Bellagio and Mandalay Bay. The hacking group, Scattered Spider, linked to the ALPHV ransomware gang, claimed responsibility. Utilizing vishing (voice phishing), the group targeted employees, gaining login credentials to deploy ransomware. MGM Resorts had suffered a previous data breach in 2019, impacting 10.6 million customers.

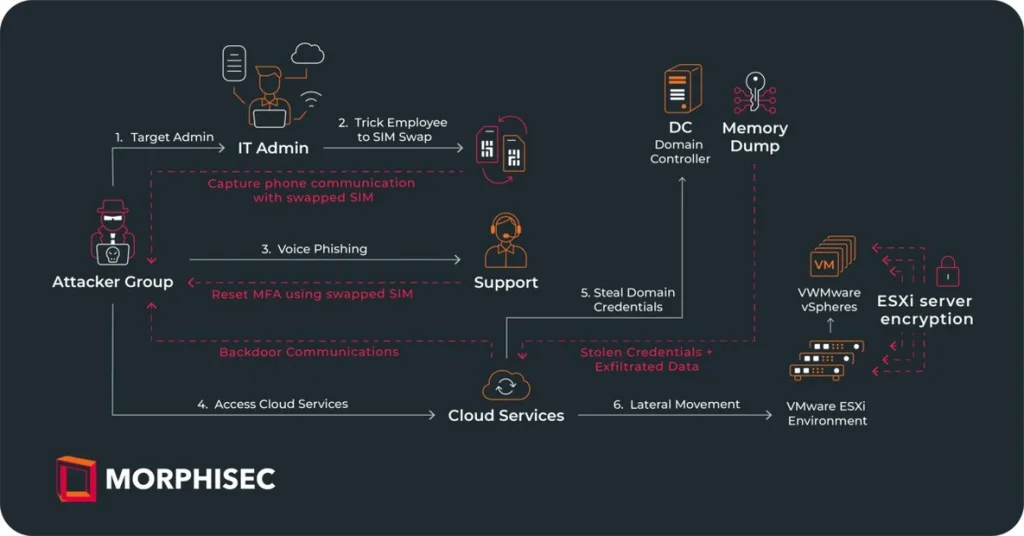
Morphisec researchers detailed a likely attack flow, involving SMS spearphishing, SIM swapping, social engineering of IT helpdesk for MFA reset codes, network access, backdoors deployment, reconnaissance, credential stealing, lateral movement, and encryption of ESXi servers.
MGM Resorts caught off guard and faced challenges in containment and response. The attackers claimed persistency with super administrator privileges and the ability to exfiltrate sensitive data.
Despite MGM’s efforts, the group successfully launched ransomware attacks on over 100 ESXi hypervisors.
The fallout included financial and reputational consequences, with ramifications for MGM’s 70,000 employees and operations in multiple states. Guests experienced issues like malfunctioning slot machines, disrupted electronic systems, elevator problems, and cash-only transactions. The hack compromised customer data, causing a $100 million impact on the company’s Q3 results. MGM Resorts shares initially fell by 4.1%, recovering slightly in the aftermath.
MGM Resorts experienced more than 36 hours of IT downtime following the ransomware attacks.
Nine days after the incident gained widespread attention, on September 19, 2023, MGM Resorts announced via Twitter that they had successfully restored their business operations.
See Also: Offensive Security Tool: Nucleimonst3r
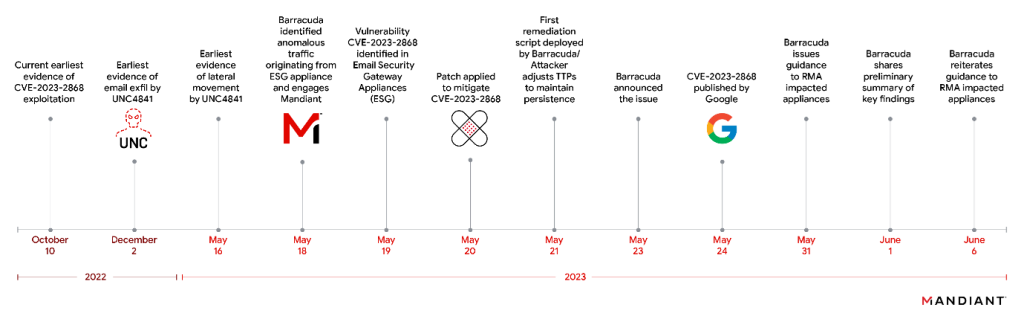
Barracuda Email Security Gateway Attacks
Barracuda made a public statement on May 23, 2023, revealing the exploitation of a previously unknown vulnerability (CVE-2023-2868) within the Barracuda Email Security Gateway (ESG).
CVE-2023-2868 stands as a critical vulnerability involving remote command injection, initially identified in Barracuda’s Email Security Gateway (ESG) product on May 19. The company issued preliminary patches on May 20 and 21. The in-the-wild exploitation was detected as far back as October 2022.
Mandiant, an incident response firm, engaged by Barracuda for the investigation, attributed the attacks to a Chinese nation-state actor labeled “UNC4841.
This entity focused on a specific group of Barracuda ESG appliances, utilizing them as a means for conducting espionage across various regions and sectors.
Starting October 10, 2022, UNC4841 initiated a campaign, sending malicious emails (Figure 2) to target organizations. These emails contained harmful attachments exploiting CVE-2023-2868 to access vulnerable Barracuda ESG appliances. UNC4841 primarily used three code families—SALTWATER, SEASPY, and SEASIDE—to establish control after exploiting CVE-2023-2868.
These families mimic legitimate Barracuda ESG modules. Post-compromise, UNC4841 aggressively targeted specific data for exfiltration and used ESG appliance access for lateral movement into victim networks. Mandiant observed UNC4841 deploying additional tools to maintain ESG appliance presence.
On June 6, 2023, Barracuda restated its guidance, advising all affected Barracuda customers to promptly isolate and substitute compromised appliances.
Figure 1: Intrusion timeline – Mandiant
Response and Mitigation Efforts
In the face of significant cybersecurity challenges posed by the incidents that occurred in 2023, organizations are advised to employ comprehensive strategies.
Immediate actions involve swiftly isolating and replacing compromised systems while enhancing incident response protocols for prompt detection and containment, especially in cases like T-Mobile and MGM Resorts.
Organizations should adopt a multifaceted approach to prioritize vulnerabilities. Emphasis should be placed on those already exploited in the wild, beginning with the CISA KEV, those with a high likelihood of exploitation (high EPSS score), and those with available weaponized exploit code.
Vendor security is crucial, requiring collaboration and stringent security measures, along with regular audits of API security protocols. Prioritizing vulnerability management involves comprehensive assessments, patching, and implementing secure coding practices. Data protection measures, including encryption, are emphasized, particularly for sensitive customer information.
Advanced threat detection tools and collaboration with threat intelligence providers are recommended for proactive defense. Ensuring regulatory compliance and establishing clear reporting mechanisms are integral components, as seen in responses to incidents like MOVEit and T-Mobile.
Internal and external penetration tests and regular cybersecurity awareness training for employees round out the multifaceted approach, collectively aimed at fortifying defenses and responding proactively to cyber threats.
Trends and Takeaways
The incidents of 2023 underscored the dynamic nature of cyber threats, the geopolitical influence on state-sponsored activities, the evolving role of emerging technologies, and the escalating impact of supply chain attacks and data breaches.
Cybercriminals demonstrated heightened sophistication, exploiting over 29,000 vulnerabilities, with a notable rise in zero-day attacks, exemplified by the TA505 group. State-sponsored actors, such as UNC4736 and UNC4857, played a pivotal role, engaging in significant operations with geopolitical implications. The year highlighted the challenges posed by emerging technologies, with the 3CX software supply chain compromise revealing vulnerabilities in widely used applications. Supply chain attacks continued to escalate, as evidenced by the MOVEit incident, emphasizing the far-reaching impact on both direct and indirect entities.
Regulatory responses and legal implications intensified, prompting mandates for prompt cybersecurity incident disclosures by public companies. The global reach of cyber threats was evident, impacting organizations worldwide and emphasizing the need for adaptive defense strategies in this dynamic cybersecurity landscape.
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to Information Security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing? If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]