Advanced Threat Actor Earth Kitsune Uses New Backdoor, WhiskerSpy

Reading Time: 3 Minutes
Watering Hole Attack
A new backdoor called WhiskerSpy has been discovered by cybersecurity firm, Trend Micro. It was used in a campaign by Earth Kitsune, an advanced threat actor known for targeting individuals interested in North Korea. The actor utilized a tried and tested tactic called a watering hole attack, where victims are picked from visitors to a pro North Korea website.
The threat actor compromised the website and injected a malicious script that asked the victim to install a video codec for the media to run.
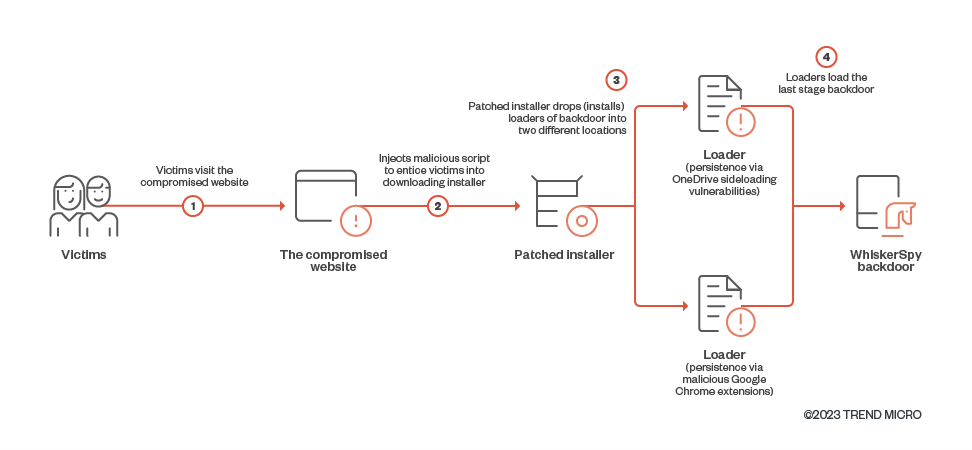 WhiskerSpy backdoor infection chain
WhiskerSpy backdoor infection chain
source: Trrend Micro
WhiskerSpy is the main payload used in Earth Kitsune’s latest campaign. It gives remote operators various capabilities, such as an interactive shell, download, upload and delete files, take screenshots, and inject shellcode into a process.
The backdoor communicates with the command and control server using a 16-byte AES key for encryption. WhiskerSpy periodically connects to the C2 for updates about its status, and the server may respond with instructions for the malware, such as executing shell commands and exfiltrating specific files.
See Also: So you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
WhiskerSpy Details
The threat actor modified a legitimate codec installer, so that it ultimately loaded “a previously unseen backdoor” on the victim’s system. The researchers say that the threat actor targeted only visitors to the website with IP addresses from Shenyang, China; Nagoya, Japan; and Brazil. The codec is an MSI executable that installs on the victim’s computer shellcode that triggers a series PowerShell commands that lead to deploying the WhiskerSpy backdoor. To achieve persistence, Earth Kitsune used the native messaging host in Google Chrome and installed a malicious Google Chrome extension called Google Chrome Helper.
The role of the extension is to allow execution of the payload every time the browser starts. Another method to achieve persistence is by leveraging OneDrive side-loading vulnerabilities that allow dropping a malicious file (fake “vcruntime140.dll”) in the OneDrive directory.
Trend Micro Tracks Earth Kitsune’s Activity
Researchers at cybersecurity company Trend Micro have been tracking Earth Kitsune’s activity since 2019. They discovered the new WhiskerSpy operation at the end of last year. The researchers note that one persistence technique that Earth Kitsune used in this campaign abuses the native messaging host in Google Chrome and installs a malicious Google Chrome extension called Google Chrome Helper. They also discovered an earlier version of WhiskerSpy that used the FTP protocol instead of HTTP for C2 communication.
 Malicious Chrome extension (Trend Micro)
Malicious Chrome extension (Trend Micro)
Trending: Exploiting LFI Vulnerabilities
Trending: Offensive Security Tool: TerminatorZ
Identifying Earth Kitsune’s Potentially New Campaign
Trend Micro’s confidence in attributing this watering hole attack to Earth Kitsune is medium, but the modus operandi and the targets are similar to activities previously associated with the group. The researchers revealed that the threat actor targeted visitors with IP addresses from Shenyang, China, Nagoya, Japan, and Brazil, although the latter was used only for testing. Relevant victims would be served a fake error message that prompts them to install a codec to watch the video.
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles or write ups about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing?
If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: bleepingcomputer.com












