BGP Hijacking Causes Brief Outage for Cloudflare’s DNS Resolver Service

Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 DNS Resolver Disrupted by BGP Hijacking and Route Leak
Cloudflare recently reported that its DNS resolver service, 1.1.1.1, experienced reachability and performance issues due to a combination of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) hijacking and a route leak. The incident, which occurred last week, affected 300 networks across 70 countries. Despite the widespread nature of the event, Cloudflare noted that the overall impact was relatively low, with many users remaining unaffected.
Details of the Incident
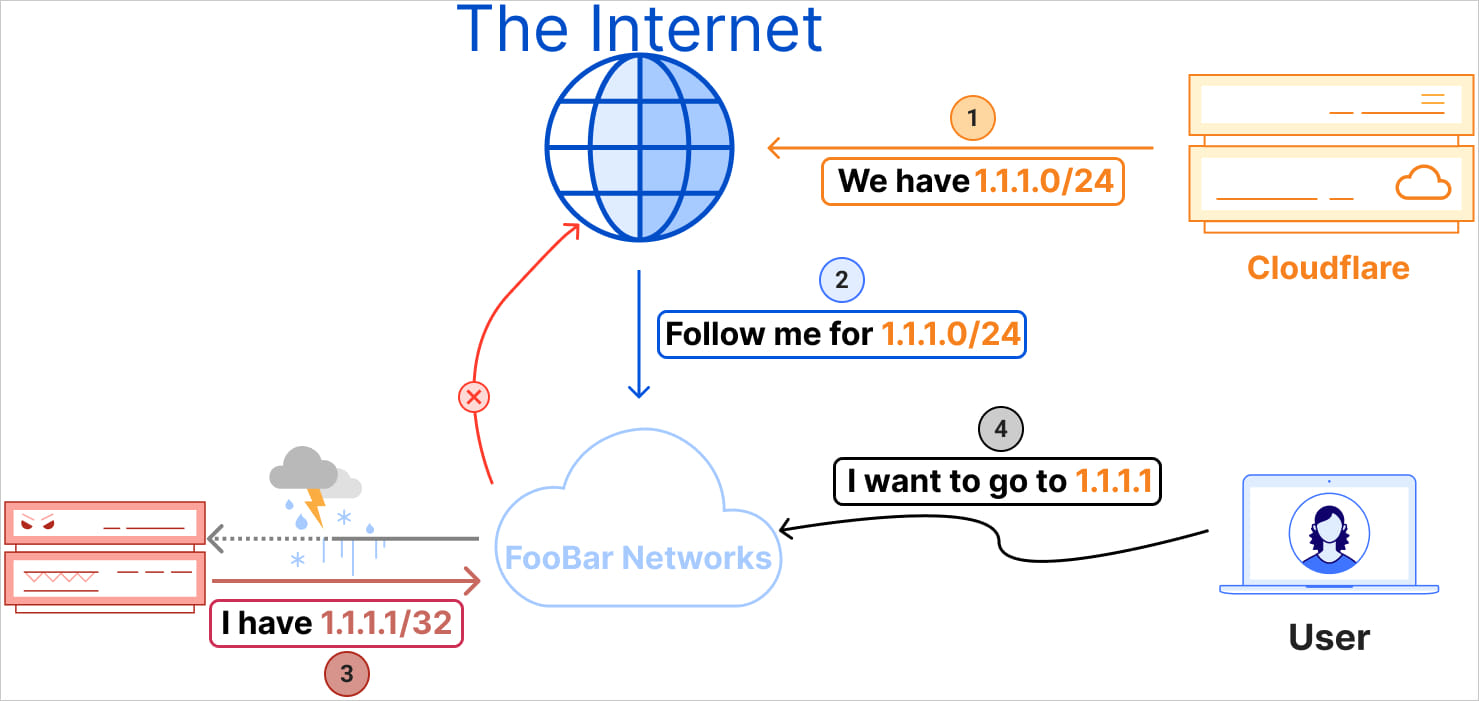
At 18:51 UTC on June 27, Eletronet S.A. (AS267613) began erroneously announcing the 1.1.1.1/32 IP address to its peers and upstream providers. This incorrect announcement was accepted by several networks, including a Tier 1 provider, which treated it as a Remote Triggered Blackhole (RTBH) route. BGP routing protocols prioritize the most specific route, causing traffic intended for Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 DNS resolver to be misrouted to AS267613 and effectively blackholed.
 Source: Cloudflare
Source: Cloudflare
A minute later, Nova Rede de Telecomunicações Ltda (AS262504) mistakenly leaked the 1.1.1.0/24 route upstream to AS1031, which further propagated the incorrect route. This compounded the initial hijacking issue, leading to additional routing and latency problems globally.
 Source: Cloudflare
Source: Cloudflare
Cloudflare identified the problem around 20:00 UTC and managed to resolve the hijack within two hours. The route leak was corrected at 02:28 UTC.
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
Remediation Efforts
In response to the incident, Cloudflare immediately engaged with the networks involved and disabled peering sessions with the problematic networks to mitigate the impact and prevent further propagation of incorrect routes. The company’s use of Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) helped mitigate the internal impact by automatically rejecting invalid routes.
Long-Term Solutions
Cloudflare’s postmortem analysis suggested several long-term measures to prevent similar incidents in the future:
- Enhancing Route Leak Detection Systems: Incorporating more data sources and integrating real-time data points to improve detection.
- Promoting RPKI Adoption: Encouraging Route Origin Validation (ROV) to enhance routing security.
- Adopting MANRS Principles: Implementing robust filtering mechanisms and rejecting invalid prefix lengths.
Trending: Digital Forensics Tool: MalStatWare
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing? If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: bleepingcomputer.com













