First Native Spectre V2 Exploit Impacts Linux Systems Running on Intel CPUs

First Native Spectre V2 Exploit Discovered, Posing Threat to Linux Systems
Security researchers have unveiled the “first native Spectre v2 exploit,” targeting Linux systems running on modern Intel processors. This new speculative execution side-channel flaw represents a significant security challenge, demonstrating ongoing complexities in addressing fundamental CPU vulnerabilities years after the original Spectre discovery.
Speculative execution, a performance optimization technique used by modern processors, involves predicting and executing future instructions before they are needed to enhance application performance. However, this optimization introduces security risks by potentially leaving traces of privileged data in CPU caches, which attackers can exploit.
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
The new Spectre v2 exploit leverages techniques such as Branch Target Injection (BTI) and Branch History Injection (BHI) to manipulate branch prediction and cause speculative execution of unauthorized code paths, leading to data leakage.
Intel has assigned CVE identifiers (CVE-2022-0001, CVE-2022-0002) to address BTI and BHI, respectively. The latest vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-2201, allows unauthenticated attackers to read arbitrary memory data through speculative execution, bypassing existing security mechanisms.
According to CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC), CVE-2024-2201 enables unauthenticated attackers to read arbitrary memory data by exploiting speculative execution, circumventing existing security mechanisms.
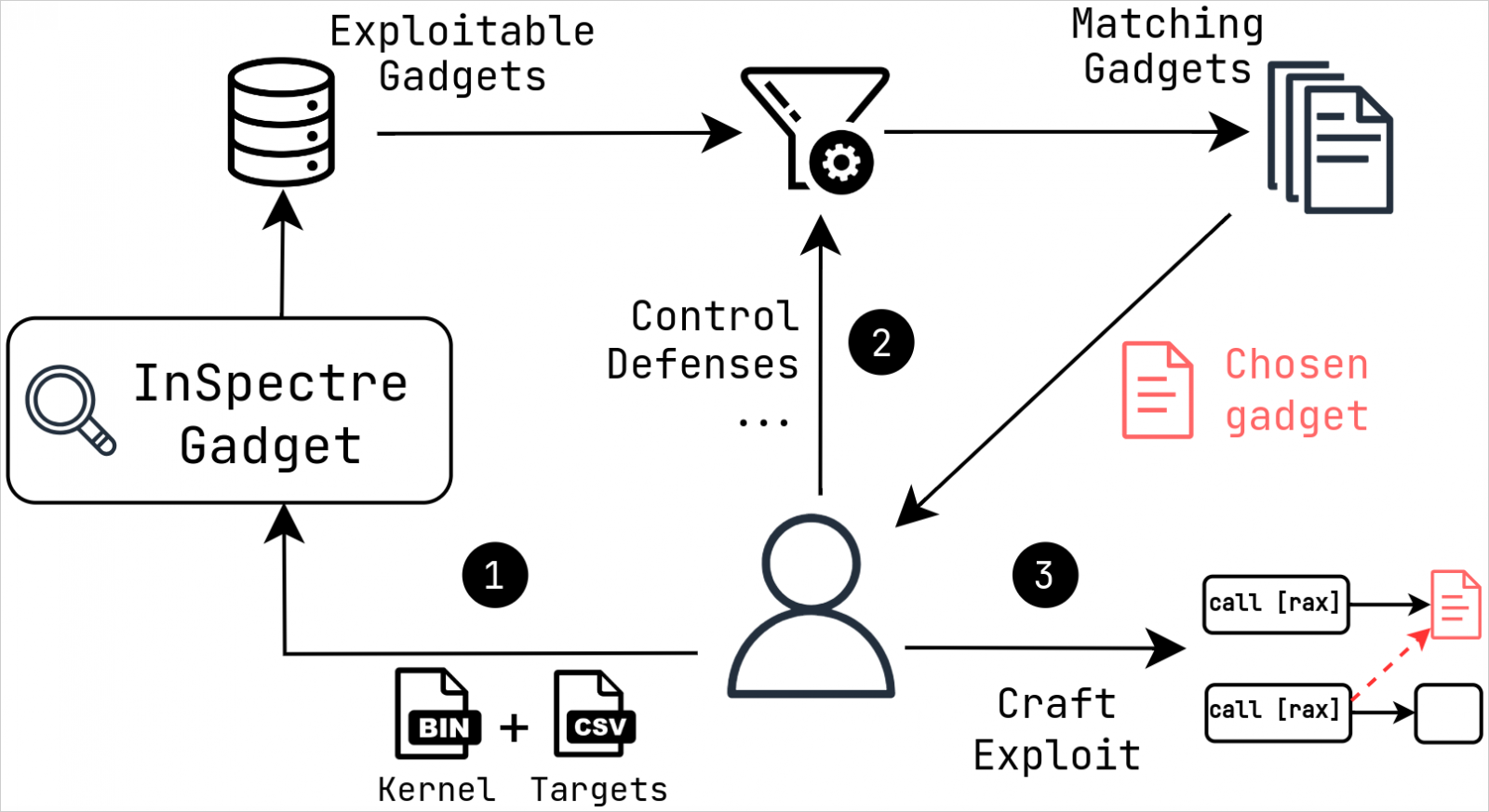
Mitigation efforts include disabling unprivileged Extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) functionality, enabling Enhanced Indirect Branch Restricted Speculation (eIBRS), and implementing Supervisor Mode Execution Protection (SMEP). Additionally, Intel recommends adding LFENCE instructions and implementing software sequences to clear the Branch History Buffer (BHB) for enhanced security.
Trending: Deep Dive to Fuzzing for Maximum Impact
Trending: OSINT Tool: NetScout


