Google Ad Platform Exploited by Fake Google Authenticator Ads

Google has fallen victim to a malicious advertising (malvertising) campaign on its own ad platform, allowing threat actors to create fake Google Authenticator ads that deliver the DeerStealer information-stealing malware.
Threat Actors Exploit Google Ads
For years, malvertising campaigns have targeted Google Search, where threat actors place ads impersonating well-known software sites to install malware on visitors’ devices. These ads often display legitimate domains, adding a false sense of trust. In a recent campaign discovered by Malwarebytes, threat actors created ads for Google Authenticator that appeared when users searched for the software on Google.
Effective Cloaking Techniques
What makes these ads particularly convincing is that they display ‘google.com’ and “https://www.google.com” as the click URL, which should not be allowed for third-party advertisements. This URL cloaking strategy has been used in previous malvertising campaigns targeting KeePass, Arc browser, YouTube, and Amazon, yet Google continues to fail in detecting and preventing these imposter ads.
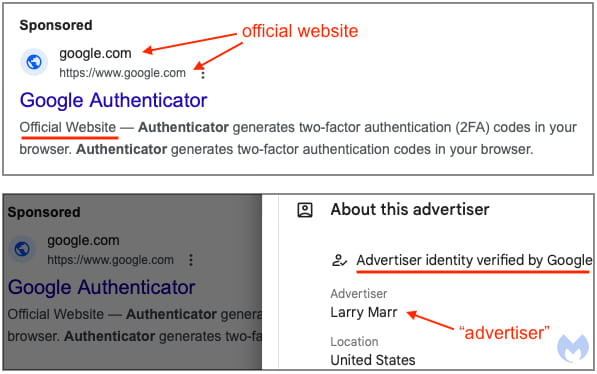 Verified advertiser account
Verified advertiser account
Source: Malwarebytes
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
Verification Loopholes
Malwarebytes noted that the advertiser’s identity is verified by Google, highlighting a significant weakness in the ad platform that threat actors exploit. When contacted about this campaign, Google reported blocking the fake advertiser identified by Malwarebytes.
Challenges in Detection
Google explained that threat actors evade detection by creating thousands of accounts simultaneously and using text manipulation and cloaking to show different websites to reviewers and automated systems. In response, Google is scaling up its automated systems and human reviewers to better detect and remove such malicious campaigns. In 2023, these efforts resulted in the removal of 3.4 billion ads, the restriction of over 5.7 billion ads, and the suspension of over 5.6 million advertiser accounts.
Fake Google Authenticator Sites
Clicking on the fake Google Authenticator ads redirects visitors through several pages to the landing page at “chromeweb-authenticators.com,” which mimics a genuine Google portal. Malware analysis firm ANY.RUN also observed this campaign, sharing additional landing pages like authenticcator-descktop[.]com, chromstore-authentificator[.]com, and authentificator-gogle[.]com.
Trending: 10 Misconceptions about Hacking
Trending: Digital Forensics Tool: Horus
Malware Delivery via GitHub
Clicking on the ‘Download Authenticator’ button on these fake sites triggers a download of a signed executable named “Authenticator.exe” hosted on GitHub. The repository hosting the malware is named ‘authgg’ by user ‘authe-gogle,’ matching the campaign’s theme.
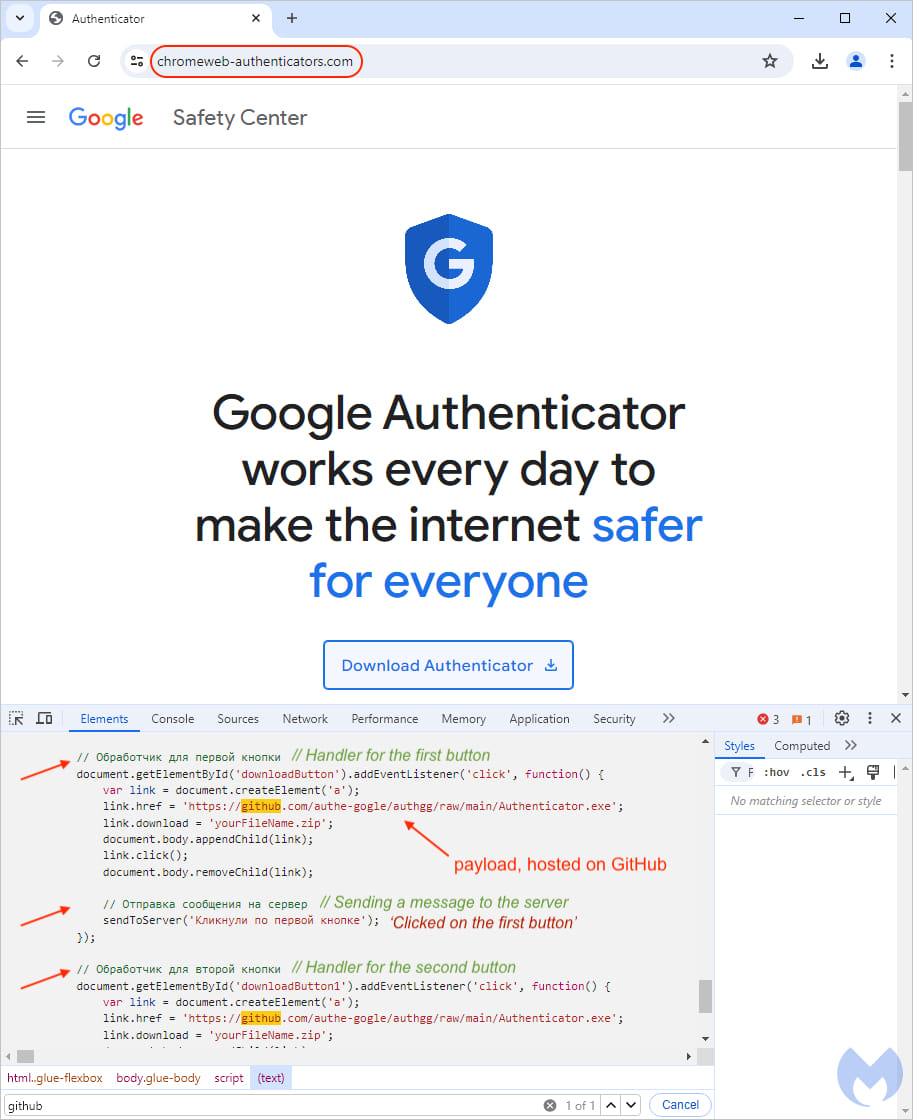 The malicious site spreading DeerStealer
The malicious site spreading DeerStealer
Source: Malwarebytes
The malware sample downloaded by Malwarebytes was signed by ‘Songyuan Meiying Electronic Products Co., Ltd.,’ enhancing its credibility and allowing it to bypass security measures on Windows.
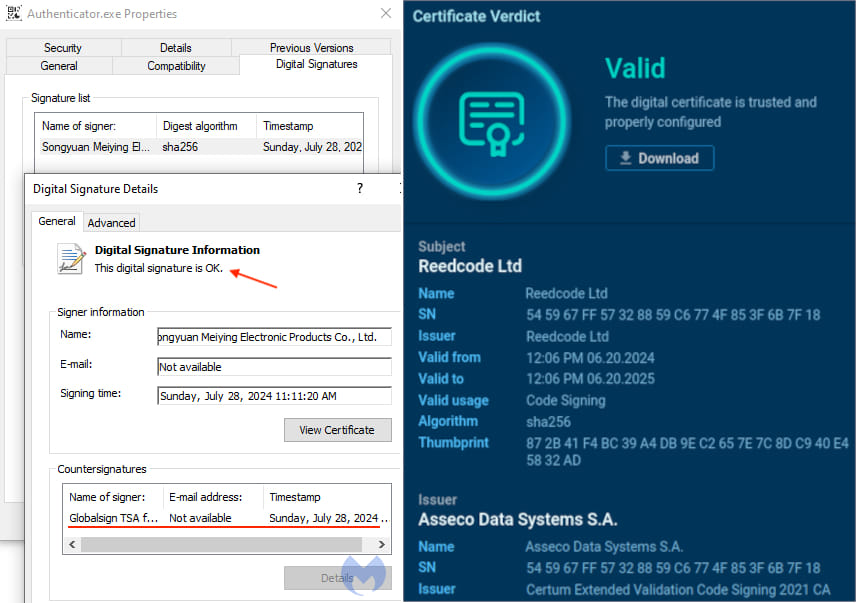 Valid signatures on different samples of the malware
Valid signatures on different samples of the malware
Source: Malwarebytes, ANY.RU
Malware Impact
Once executed, the download launches the DeerStealer information-stealing malware, which captures credentials, cookies, and other information stored in the user’s web browser.
Recommendations for Users
Users are advised to avoid clicking on promoted results on Google Search, use an ad blocker, or bookmark the URLs of software projects they frequently use. Before downloading any files, ensure the URL corresponds to the official domain of the project, and always scan downloaded files with up-to-date antivirus tools before executing them.
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing? If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: bleepingcomputer.com













