Hackers Exploit Ivanti Vulnerability to Deploy DSLog Backdoor

In a recent development, hackers are capitalizing on a server-side request forgery (SSRF) vulnerability present in Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA gateways to deploy a newly identified backdoor named DSLog on susceptible devices.
The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-21893, was disclosed as an actively exploited zero-day on January 31, 2024. Ivanti responded by sharing security updates and mitigation guidance to address the flaw, which impacts the SAML component of the affected products.
Successful exploitation of CVE-2024-21893 enables attackers to circumvent authentication measures and gain unauthorized access to restricted resources on Ivanti gateways running versions 9.x and 22.x. To remedy the issue, Ivanti has released updates for Connect Secure versions 9.1R14.4, 9.1R17.2, 9.1R18.3, 22.4R2.2, 22.5R1.1, and 22.5R2.2, Policy Secure version 22.5R1.1, and ZTA version 22.6R1.3.
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
On February 5, 2024, threat monitoring service Shadowserver observed multiple attackers attempting to exploit the vulnerability, some utilizing proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits previously published by Rapid7. However, the success rate of these attacks remains undetermined.
Further investigation by Orange Cyberdefense confirmed the exploitation of CVE-2024-21893 to install the DSLog backdoor, allowing threat actors to execute remote commands on compromised Ivanti servers. Orange researchers discovered the presence of DSLog on a compromised appliance on February 3, 2024, after analyzing a device that had implemented Ivanti’s XML mitigation but had not applied the patch.
The DSLog backdoor operates by injecting encoded commands into SAML authentication requests, enabling attackers to execute operations such as system information retrieval and filesystem permissions manipulation. Notably, the backdoor employs a unique SHA256 hash per appliance as an API key, ensuring authentication of commands sent via HTTP requests.
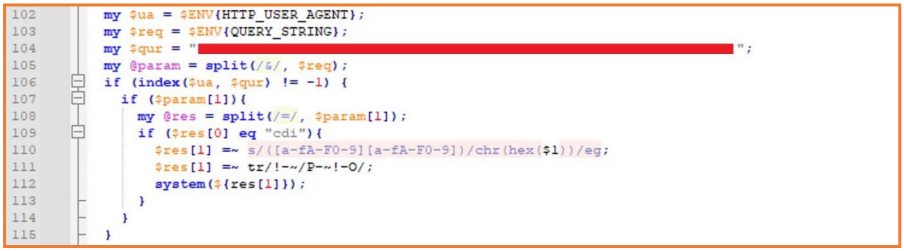 Backdoor injection into the DSLog file (Orange)
Backdoor injection into the DSLog file (Orange)
Trending: Jeff Foley – OWASP Amass Founder
Trending: Recon Tool: go-dork


