Malicious Chrome ad blocker injects ads behind the scenes

Reading Time: 1 Minute
The AllBlock Chromium ad blocking extension has been found to be injecting hidden affiliate links that generate commissions for the developers.
This extension is still available on Chrome’s Web Store and promotes itself as an ad blocker that focuses on YouTube and Facebook to prevent pop-ups and speed up browsing.
However, according to researchers at Imperva, the extension is actually conducting a deceptive ad-injection campaign that causes legitimate URLs to redirect to affiliate links controlled by the extension’s developers.
Ad injection is the process of inserting advertisements or links into a web page that doesn’t normally host them, allowing the scammers to make money from advertisements or redirect people to affiliate sites to earn commissions.
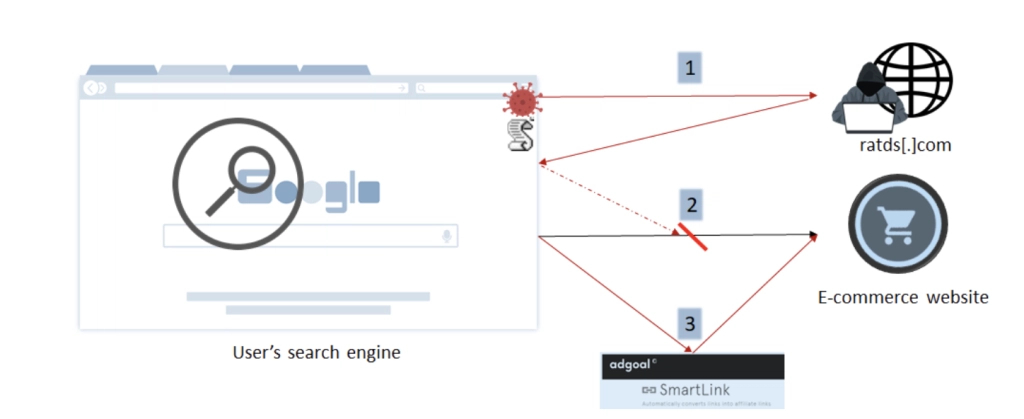
Source: Imperva
See Also: Complete Offensive Security and Ethical Hacking Course
In August 2021, Imperva’s researchers discovered a set of previously unknown malicious domains distributing an ad injection script.
This malicious script would send legitimate URLs to a remote server and receive a list of redirection domains as a response. If a user clicks on an altered link, the user is redirected to a different page, typically, an affiliate link.
The ad-injecting script even features evasion techniques such as excluding large Russian search engines, clearing the debugging console every 100 ms, and active detection of initialized Firebug variables.
By taking a deeper look at AllBlock, Imperva’s team found the script they were hunting for in “bg.js,” which injects code into every new tab opened on the browser.
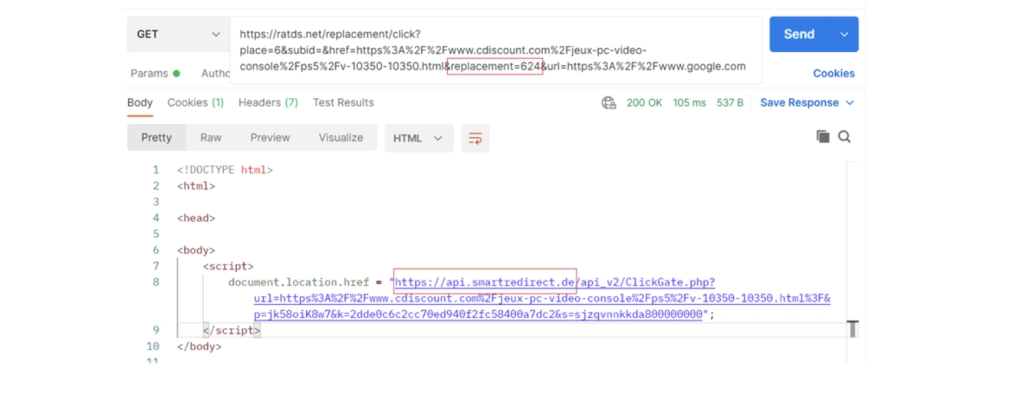
Source: Imperva
See Also: Apple Pay with VISA lets hackers force payments on locked iPhones
To inject the malicious script, the extension would connect to an URL at allblock.net, which would return a base64 encoded script that would be decoded and injected into the webpage.
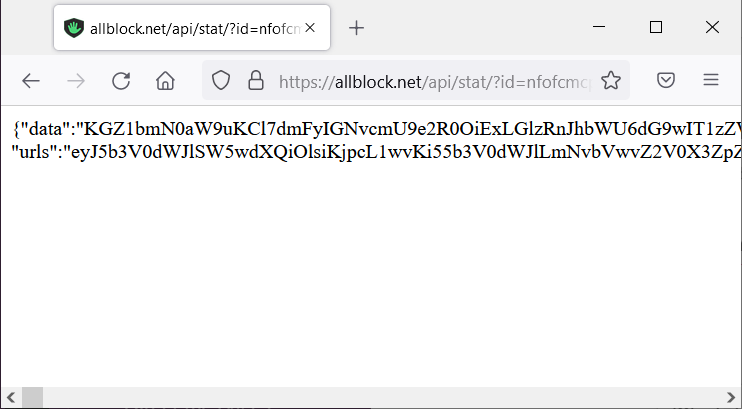
The developers of the extension have added several innocuous objects and variables into the malicious JavaScript snippet in an attempt to obfuscate the code execution.
How the extension is promoted is currently unclear, and Imperva believes that the scammers may also utilize other extensions in this campaign.
“We do not believe we found the origin of the attack that led us to this discovery, likely because of the way the script was injected. The script we first observed was injected via a script tag pointing to a remote server where the AllBlock extension injects the malicious code directly to the active tab, Imperva explains in the report.
This leads us to believe that there is a larger campaign taking place that may utilize different delivery methods and more extensions.” – Imperva.
See Also: Offensive Security Tool: Whispers
See Also: Hacking stories – Operation Aurora: When China hacked Google
Source: www.bleepingcomputer.com
(Click Link)










