New Cuttlefish Malware Hijacks Router Traffic to Harvest Credentials

A newly discovered malware named ‘Cuttlefish’ has emerged, posing a significant threat to both enterprise-grade and small office/home office (SOHO) routers. Lumen Technologies’ Black Lotus Labs has conducted an in-depth analysis of this malware, revealing its alarming capabilities.
Cuttlefish operates by infiltrating routers and establishing a proxy or VPN tunnel, allowing it to stealthy monitor data passing through the compromised devices. This sophisticated approach enables the malware to bypass security measures that typically detect unusual sign-ins.
Furthermore, Cuttlefish can execute DNS and HTTP hijacking within private IP spaces, disrupting internal communications and potentially introducing additional malicious payloads.
While Cuttlefish shares some code similarities with HiatusRat, a malware previously associated with Chinese state interests, no direct links have been established between the two, making attribution challenging.
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
According to Black Lotus Labs, Cuttlefish has been active since at least July 2023, primarily targeting routers in Turkey. However, isolated infections have also been reported in satellite phone and data center services globally.
Cuttlefish Infection chain
Cuttlefish infects routers by exploiting vulnerabilities or using brute-force attacks to gain access. Once inside, it deploys a bash script (“s.sh”) to collect host-based data like directory listings and active connections.
The script then downloads and executes the primary Cuttlefish payload (“.timezone”), which operates in memory to avoid detection. Cuttlefish is versatile, with builds supporting various router architectures, making it a significant threat to network security.
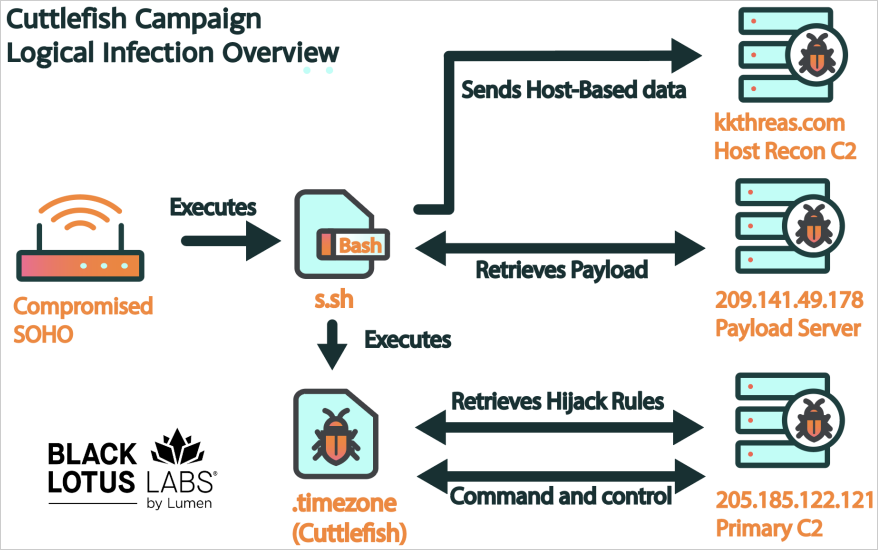 Infection chain
Infection chain
Source: Black Lotus Labs
Monitoring Traffic
Cuttlefish monitors traffic by employing a packet filter to track all connections passing through the infected device. It scans for specific data, like usernames, passwords, and tokens associated with cloud-based services, in the intercepted packets. This information is then logged locally and eventually exfiltrated to the attacker’s command and control server.
 Proxy functionality
Proxy functionality
Source: Black Lotus Labs
Trending: Deep Dive to Fuzzing for Maximum Impact
Trending: OSINT Tool: Certina
Evading Detection
To evade detection, Cuttlefish creates a peer-to-peer VPN or proxy tunnel on the compromised device for data transmission. Additionally, it redirects DNS requests and manipulates HTTP traffic to control communication and potentially hijack internal or site-to-site traffic, granting access to secured resources typically inaccessible via the public internet.
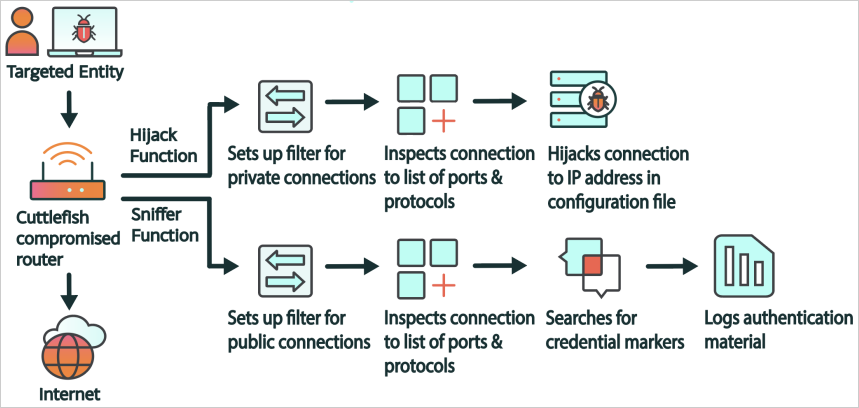
Cuttlefish operational diagram
Source: Black Lotus Labs
Protecting from Cuttlefish
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing? If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: bleepingcomputer.com













