Over 16,000 Fortinet Devices Compromised with Stealth Symlink Backdoor

See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
Impact and Exposure
Devices affected include FortiGate systems with SSL-VPN enabled that were previously compromised and later patched. However, due to the stealthy nature of the symlink, threat actors retain access to sensitive data such as:
Device configurations
User credentials
System files
These symlinks do not rely on new vulnerabilities, making detection and remediation particularly challenging.
Detection & Mitigation
Fortinet has released:
New AV/IPS signatures to detect and remove the malicious symlink.
Updated firmware that:
Removes the symbolic link if present
Blocks unknown folders and files from being served via the device’s webserver
Fortinet has also begun notifying affected customers privately by email based on detections by FortiGuard.
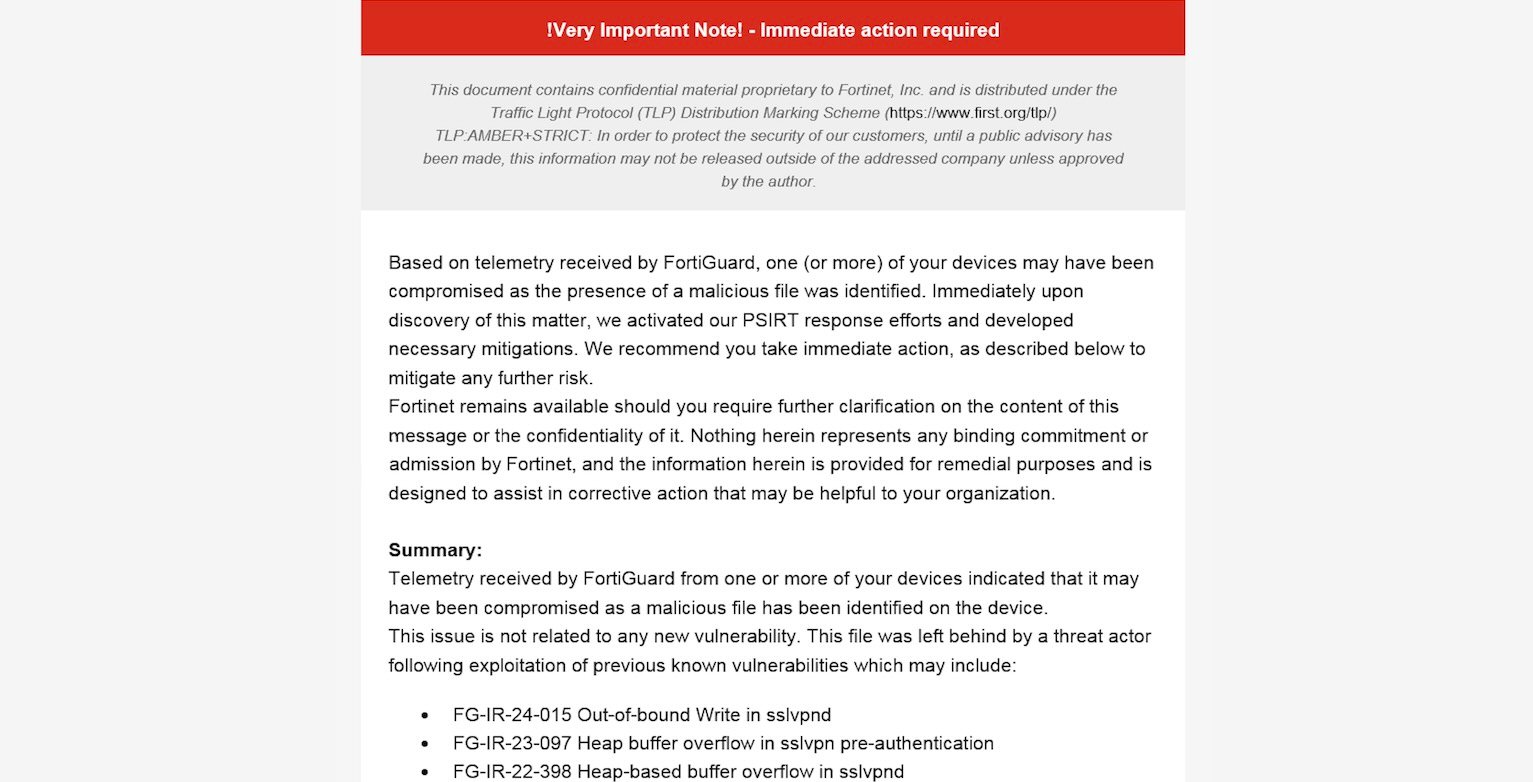 Emails sent to owners of compromised devices
Emails sent to owners of compromised devices
Source: BleepingComputer
Trending: Recon Tool: spoof_checker
Recommended Actions for Affected Admins
If your FortiGate device has been identified as compromised, Fortinet strongly recommends performing a full clean installation rather than relying on patching alone.
Reinstallation & Restoration
Download the latest firmware from the Fortinet Support site.
Verify firmware integrity using SHA512 checksums.
See: Technical Tip – How to verify downloaded firmware checksum using SHA512.Format the device flash and perform a clean install using TFTP.
See: Technical Tip – Loading a FortiGate firmware image using TFTP.After TFTP reinstallation, format the disk partition to fully remove potential remnants.
See: Technical Tip – Standard procedure to format a FortiGate Log Disk.
Post-Restoration Hardening
Do not reuse the existing configuration file unless it’s from a known clean backup.
Reset all credentials, including:
Admin and local user accounts
VPN user credentials
RADIUS secrets
IPsec pre-shared keys (PSKs)
Replace all certificates, and revoke any that may have been exposed.
Change GUI admin port from the default (TCP 443) to a custom port.
Restrict administrative logins to trusted IPs only.
Disable GUI/CLI access on any Internet-facing interfaces.
Perform administrative tasks on an out-of-band management network only.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) across all admin accounts.
Change any LDAP user credentials used for device authentication.
Apply all recommendations in the FortiOS Hardening Guide.
Immediately upgrade to the latest FortiOS version after restoring the config to ensure the device is not left exposed on older firmware.
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing? If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: bleepingcomputer.com













