Rilide: The Malicious Extension that Steals Cryptocurrency and Bypasses 2FA

Malicious browser extension Rilide
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new malicious browser extension that targets several popular browsers. The malware, called Rilide, is capable of monitoring browser activity, taking screenshots, and stealing cryptocurrency by injecting scripts into web pages. Rilide hides in plain sight by mimicking benign Google Drive extensions and abusing built-in Chrome functionalities.
Trustwave SpiderLabs detected two separate campaigns distributing Rilide. One campaign used Google Ads and Aurora Stealer to load the extension using a Rust loader, while the other distributed the malicious extension using the Ekipa remote access trojan (RAT). Although the malware’s origin is unknown, Trustwave reports that it has similarities with similar extensions sold to cybercriminals. Portions of Rilide’s code were also recently leaked on an underground forum due to a dispute between cybercriminals over unresolved payment.
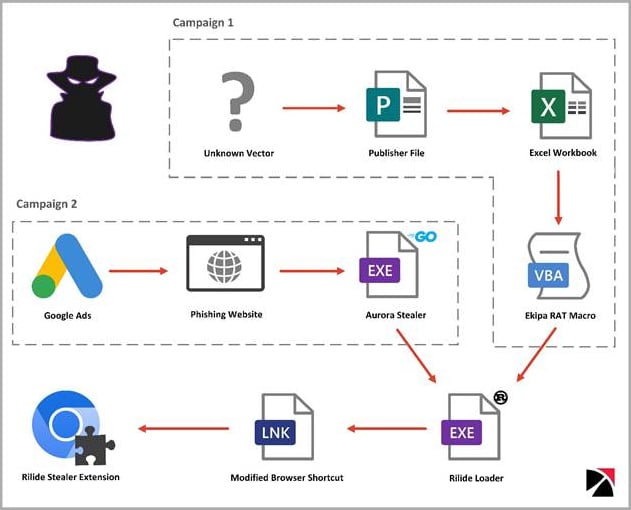 Two campaigns pushing Rilide (Trustwave)
Two campaigns pushing Rilide (Trustwave)
See Also: So you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
How Rilide works
Rilide’s loader modifies web browser shortcut files to automate the execution of the malicious extension that drops onto the compromised system. Once executed, the malware runs a script to attach a listener that monitors when the victim switches tabs, receives web content, or when webpages finish loading. Rilide also checks if the current site matches a list of targets available from the command and control (C2) server. If there is a match, the extension loads additional scripts injected into the webpage to steal information related to cryptocurrencies, email account credentials, and more.
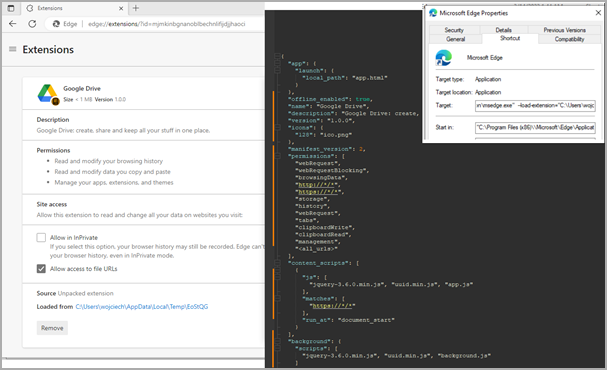 Malicious extension on Edge (Trustwave)
Malicious extension on Edge (Trustwave)
In addition to the above, the extension disables ‘Content Security Policy’, a security feature designed to protect against cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. This allows Rilide to load external resources that the browser would normally block. The extension also regularly exfiltrates browsing history and can capture screenshots and send them to the C2.
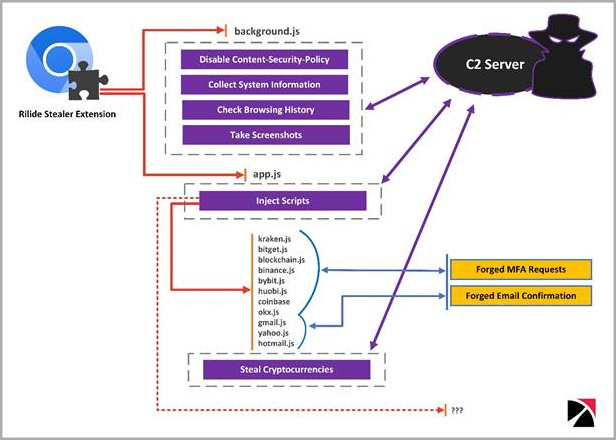 Rilide’s capabilities graph (Trustwave)
Rilide’s capabilities graph (Trustwave)
Trending: Offensive Security Tool: Nginxpwner
Rilide’s 2FA-bypassing system
Rilide’s 2FA-bypassing system is particularly concerning. The malware uses forged dialogs to deceive victims into entering their temporary codes. The system is activated when the victim initiates a cryptocurrency withdrawal request to an exchange service that Rilide targets. The malware then injects the script in the background and processes the request automatically. Once the user enters their code on the fake dialog, Rilide uses it to complete the withdrawal process to the threat actor’s wallet address.
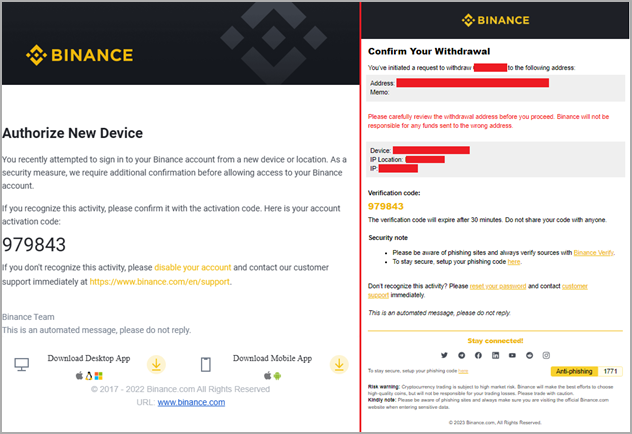 Replacing the legitimate email (right) while extracting the 2FA code (Trustwave)
Replacing the legitimate email (right) while extracting the 2FA code (Trustwave)
Trustwave warns that while the roll-out of Manifest v3 on all Chromium-based browsers will improve resistance against malicious extensions, it won’t eliminate the problem. Rilide showcases the growing sophistication of malicious browser extensions that now come with live monitoring and automated money-stealing systems. It’s crucial for users to protect themselves by being vigilant and using reputable anti-malware software when browsing the internet.
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles or write ups about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing?
If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: thehackernews.com












