OSINT Tool: ProtOSINT

ProtOSINT
ProtOSINT is a Python script that helps you investigate ProtonMail accounts and ProtonVPN IP addresses.
Description
This tool can help you in your OSINT investigation on Proton service (for educational purposes only).
ProtOSINT is separated in 3 sub-modules:
- [1] Test the validity of one protonMail account and get additional information
- [2] Try to find if your target have a protonMail account by generating multiple adresses by combining information fields inputted
- [3] Find if your IP is currently affiliate to ProtonVPN
See Also: So you want to be a hacker?
Complete Offensive Security and Ethical Hacking Course
Important update of the ProtonMail API
- The API now seems to be limited to a few queries (ten/fifteen requests).
- The blocking time is one hour (the limitation seems to be by IP address).
- Even if an email is not valid, the API will return a result that seems valid with a random timestamp.
- However, if the email is really valid, the timestamp returned is still good.
Advice for using ProtOSINT nowadays
- Use only module 1 and 3.
- Before using module 1, first test the validity of your email with a third party tool or with the recipient field directly in the ProtonMail web interface:
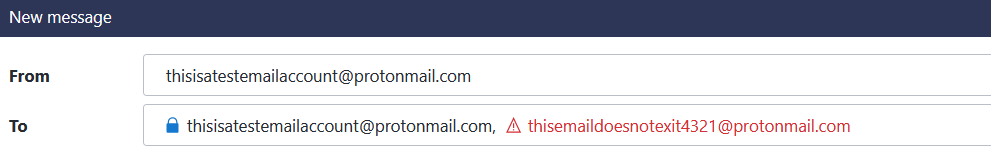
Then, using ProtOSINT, get additional information (the public key attached to the email, the date the PGP key was created and the encryption used).
Prerequisite
Usage
python3 protosint.py
Trending: Recon Tool: BF ActiveSub
Tips for ProtonMail Investigation
ProtonMail is case-insensitive
The account name in the ProtonMail is case-insensitive and ProtonMail considers the “.” “_” “-” symbols as transparent.
Additionnaly, any words put after a “+” sign are not taken into account.
It means that all of these email adresses below are the same as [email protected]:
All of these emails have the save timestamp and refers to the account [email protected].
Timestamp
ProtOSINT does not always give you the creation time of the ProtonMail account itself. The timestamp returned by ProtonMail API is the time and date when the primary PGP key for the email was created.
Example 1: my target keeps the default settings
In this case, ProtOSINT gives me the real date of creation of the ProtonMail account.
- 2021-01-12: Creation of the protonmail account “[email protected]“
Fingerprint of the key: 382a2045a09305f5ab4ef9000e1a2dd1e7e162fe – RSA (2048).
- 2021-01-15: ProtOSINT gives me the 2021-01-12 timestamps
Example 2: my target changes the email encryption keys
In this case, ProtOSINT does not give me the “real” date of creation of the ProtonMail account but the date of creation of the primary PGP key.
- 2021-01-12: Creation of the protonmail account “[email protected]“
Fingerprint of the key: 382a2045a09305f5ab4ef9000e1a2dd1e7e162fe – RSA (2048).
- 2021-01-13: My target changes the primary PGP key (in settings/keys/Email encryption keys)
New fingerprint of the key: 634936a85115b8e30a31b94345d4551bc66da9d3 – RSA (2048).
- 2021-01-15: ProtOSINT gives me the 2021-01-13 timestamp and not the other (2021-01-12)
Email encryption keys
ProtOSINT allow you to know which encryption key is used for a ProtonMail account:
- RSA 2048-bit (Older but faster) – high security
- RSA 4096-bit (Secure but slow) – highest security
- X25519 (Modern, fastest, secure) – State-of-the-art
Custom domain
In the first sub-module of ProtOSINT [1], you can import a custom domain like [email protected]. In fact, the premium ProtonMail plan allows you to connect your custom domain to ProtonMail. This means that if [email protected] is “valid”, your target uses a premium ProtonMail account.
Clone the repo from here: GitHub Link