Recon Tool: RADAR
Reading Time: 4 Minutes
RADAR: Rapid Assessment of DNS And Reconnaissance
RADAR, developed by gvukov, is an advanced DNS reconnaissance tool designed to identify technologies and services used by domains through their DNS footprints. It can detect hundreds of technologies including cloud services, email providers, CDNs, security services, and more.
Features
- Comprehensive DNS Scanning: Queries all relevant DNS record types (A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, TXT, NS, SOA, SRV, CAA, etc.)
- Technology Detection: Identifies technologies using pattern matching against an extensive signature database
- Performance Optimized: Uses parallel queries and multiple resolvers for efficient scanning
- Extensible: Easy to add new technology signatures via the JSON signature database
- Detailed Reporting: Produces structured JSON output for easy integration with other tools
- Robust Resolving: Leverages both system DNS resolver and public DNS services for maximum coverage
- Auto-Updates: Automatically downloads the latest signatures from GitHub
- Batch Scanning: Process multiple domains from a list with a single command
See Also: So you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security and Ethical Hacking Course
Installation
Run the following command to install the latest version:
go install -v github.com/Elite-Security-Systems/radar/cmd/radar@latest
Using Prebuilt Binaries
Download the latest release for your platform from the releases page.
Using Docker
Pull and run the Docker image:
docker pull elitesecuritysystems/radar:latest
docker run elitesecuritysystems/radar -domain example.com
From Source
# Clone the repository git clone https://github.com/Elite-Security-Systems/radar.git cd radar # Build go build -o radar ./cmd/radar # Install (optional) go install ./cmd/radar
Quick Start
# Basic domain scan radar -domain example.com # Scan with all DNS records in output radar -domain example.com -all-records # Scan multiple domains from a file radar -l domains.txt # Use custom signatures file radar -domain example.com -signatures /path/to/signatures.json # Enable debug output radar -domain example.com -debug # Set custom timeout radar -domain example.com -timeout 30
Output Options
Clean JSON Output
By default, RADAR provides clean JSON output with no progress indicators or separators, making it ideal for piping to other tools:
# Basic usage radar -domain example.com > result.json # Multiple domains radar -l domains.txt > all-results.json
When processing multiple domains, each domain’s result will be output as a complete JSON object, one after another.
Verbose Output Mode
If you prefer to see progress information when processing multiple domains, use the -verbose flag:
radar -l domains.txt -verbose
This will display progress information on stderr while keeping the stdout output clean:
Processing domain 1/3: example.com
Processing domain 2/3: example.org
Processing domain 3/3: example.net
The JSON output will still be sent to stdout, making it easy to redirect while still seeing progress:
radar -l domains.txt -verbose > results.json
Saving Results to Files
You can save results directly to files using the -o flag:
# Save to a specific file radar -domain example.com -o results.json # Save to a directory (creates timestamped files for each domain) radar -l domains.txt -o ./results/
With the -verbose flag, you’ll see information about where files are saved:
radar -l domains.txt -o ./results/ -verbose Processing domain 1/3: example.com Results for example.com saved to: ./results/example.com_20250410-150405.json Processing domain 2/3: example.org Results for example.org saved to: ./results/example.org_20250410-150406.json ...
Target List Functionality
RADAR supports scanning multiple domains using a target list file with the -l flag:
# Scan multiple domains from a file
radar -l domains.txt
Where domains.txt contains one domain per line:
example.com
example.org
example.net
Output Options with Target Lists
When using a target list, RADAR provides flexible output options:
Standard Output (No -o flag) Results for each domain are printed to stdout sequentially as clean JSON.
Directory Output (Directory Path)
radar -l domains.txt -o results/
Creates separate files for each domain.
Combined Output (Specific File Path)
radar -l domains.txt -o combined-results.json
Saves all results to a single combined JSON file.
Target List Format
- One domain per line
- Empty lines are ignored
- Lines starting with # are treated as comments
Example:
# Production domains
example.com
example.org
# Development domains
dev.example.com
staging.example.com
Silent Mode
Use the -silent flag to suppress all output except error messages:
# Silent mode with output to a file radar -domain example.com -o results.json -silent # No output appears if successful, only errors would be shown
This is particularly useful for:
- Scheduled tasks and cron jobs
- CI/CD pipelines
- Batch processing where you want to avoid any output
Advanced Usage
Updating Signatures
RADAR automatically manages signature files, downloading the latest from GitHub when needed. You can force an update with:
radar -update-signatures
Including All DNS Records
By default, RADAR only includes detected technologies in the output. You can include all DNS records with:
radar -domain example.com -all-records
Batch Processing Example
#!/bin/bash OUTPUT_DIR="./results" mkdir -p "$OUTPUT_DIR" # Read domains from a file while read domain; do echo "Processing $domain..." radar -domain "$domain" -o "$OUTPUT_DIR" -silent if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo " Successfully analyzed $domain" else echo " Failed to analyze $domain" fi done < domains.txt echo "All scans complete. Results saved in $OUTPUT_DIR directory."
For more advanced batch processing, use the built-in target list functionality:
radar -l domains.txt -o combined-results.json -verbose
Docker Usage
Basic Usage
docker run elitesecuritysystems/radar -domain example.com
With Target List
docker run -v "$(pwd)/domains.txt:/domains.txt" \
elitesecuritysystems/radar -l /domains.txt
Save Results to Host Machine
docker run -v "$(pwd)/output:/output" -v "$(pwd)/domains.txt:/domains.txt" \ elitesecuritysystems/radar -l /domains.txt -o /output
Verbose Mode with Docker
docker run -v "$(pwd)/domains.txt:/domains.txt" \
elitesecuritysystems/radar -l /domains.txt -verbose
Silent Mode with Docker
docker run -v "$(pwd)/output:/output" \
elitesecuritysystems/radar -domain example.com -o /output -silent
Force Update Signatures
docker run elitesecuritysystems/radar -update-signatures
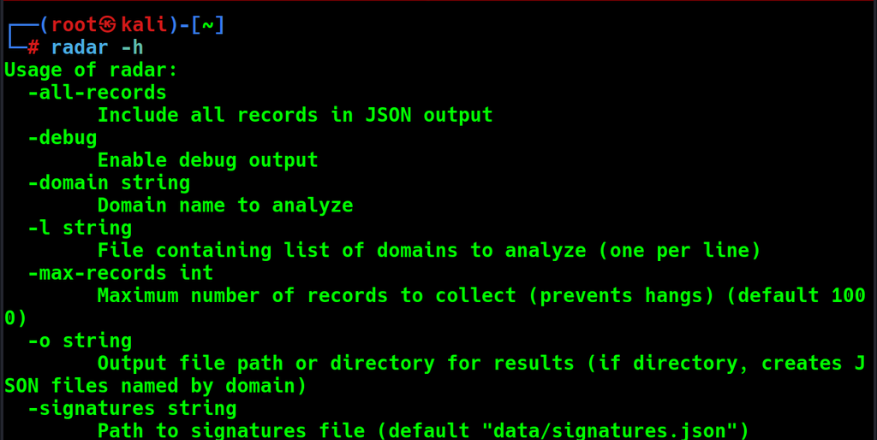
Command Line Options
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
-domain | Domain name to analyze |
-l | File containing list of domains to analyze (one per line) |
-o | Output file path or directory for results |
-all-records | Include all records in JSON output |
-timeout | Query timeout in seconds (default: 15) |
-debug | Enable debug output |
-max-records | Maximum number of records to collect (default: 1000) |
-signatures | Path to signatures file (default: data/signatures.json) |
-update-signatures | Force update signatures from GitHub |
-silent | Silent mode – suppress all output |
-verbose | Show progress information on stderr while keeping clean JSON on stdout |
-version | Show version information |
Custom Signatures
RADAR uses a JSON-based signature format for technology detection. You can extend the default signature set or create your own:
{
"signatures": [
{
"name": "My Custom Technology",
"category": "Web Platform",
"description": "Description of the technology",
"recordTypes": ["TXT", "CNAME"],
"patterns": [
"regex-pattern-to-match",
"another-pattern-.*"
],
"website": "https://example.com"
}
]
}
Building the Docker Image
If you want to build the image yourself:
# Clone the repository git clone https://github.com/Elite-Security-Systems/radar.git cd radar # Build using the provided script chmod +x build-push.sh ./build-push.sh # Or build and push to Docker Hub ./build-push.sh --push
Clone the repo from here: GitHub Link