Static Code Analysis Tool: scanmycode-ce

Reading Time: 5 Minutes
Static Code Analysis Tool: scanmycode-ce
Static Code Analysis is the process of auditing the source code of an application to identify security vulnerabilities. The assessment ensures whether or not all necessary controls are in place (filtering of input data, range checks, data type checks, encryption, etc) and, that they work as intended. It is a way of ensuring that the application developed is secure and self-defending in the given environment.
This tool will help Security Researchers, Pentesters and the Red Team understand how source code review can be the best way of identifying those vulnerabilities that may have gone undetected during the process of application security testing or penetration testing.
What it does
scanmycode by Marcinguy, is a Code Scanning/SAST/Static Analysis/Linting solution using many tools/Scanners with One Report. You can also add any tool to it. Currently, it supports many languages and tech stacks. Similar to SonarQube, but it is different. The main difference is that you can connect external tools to it, and really much more.
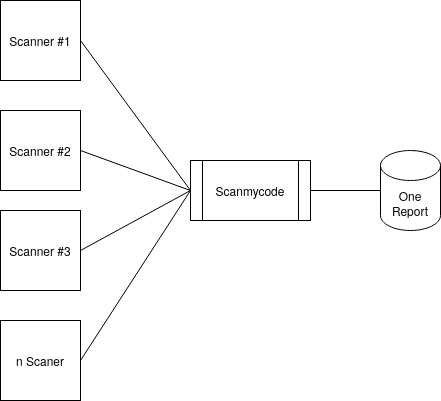
Fig. 1 Scanmycode concept diagram
See Also: Offensive Security Tool: KeeThief
TLDR;
To install it. Install docker and docker-compose and then:
2 options
- Fastest (use DockerHub built images). If unsure, use this.
git clone https://github.com/marcinguy/scanmycode-ce.gitcd scanmycode-ce/dockerhub
./start.sh
- Slower (build everything)
git clone https://github.com/marcinguy/scanmycode-ce.gitcd scanmycode-ce/docker./start.sh
Go in the Browser to:
http://localhost:5000
Sign up locally (and login in when needed)
More info in the Wiki:
https://github.com/marcinguy/scanmycode-ce/wiki
Under the hood
Progpilot, PMD, Bandit, Brakeman, Gosec, confused, semgrep, trufflehog3, jshint, log4shell via custom semgrep rule and other(s). Some were modified.
How is Scanmycode different than SonarQube?
Both use static analysis to find bugs and defects, but there are a few differences.
- Scanmycode can be extended with any tool producing JSON output (any binary, in any technology/language/product). That’s the biggest difference.
- Scanmycode is Open Source, SonarQube also offers an open-source version, but it is missing features (For example, 12 of the supported languages are not available in the open-source offering, and more powerful dataflow features are only available in the paid versions)
- Scanmycode supports scanning only changed files (differential analysis), SonarQube does not
- Scanmycode uses also semgrep as one of the tools (without semgrep community rules, only Scanmycode’s custom rules)
Below are semgrep’s (also Scanmycode advantages over SonarQube):
“Extending Semgrep with custom rules is simple, since Semgrep rules look like the source code you’re writing. Writing custom rules with SonarQube is restricted to a handful of languages and requires familiarity with Java and abstract syntax trees (ASTs).”
“Semgrep focuses on speed and ease-of-use, making analysis possible at up to 20K-100K loc/sec per rule. SonarQube authors report approximately 0.4K loc/sec for rulesets in production.”
Source: semgrep’s website
See Also: Complete Offensive Security and Ethical Hacking Course
Even more screenshots from scanning real projects
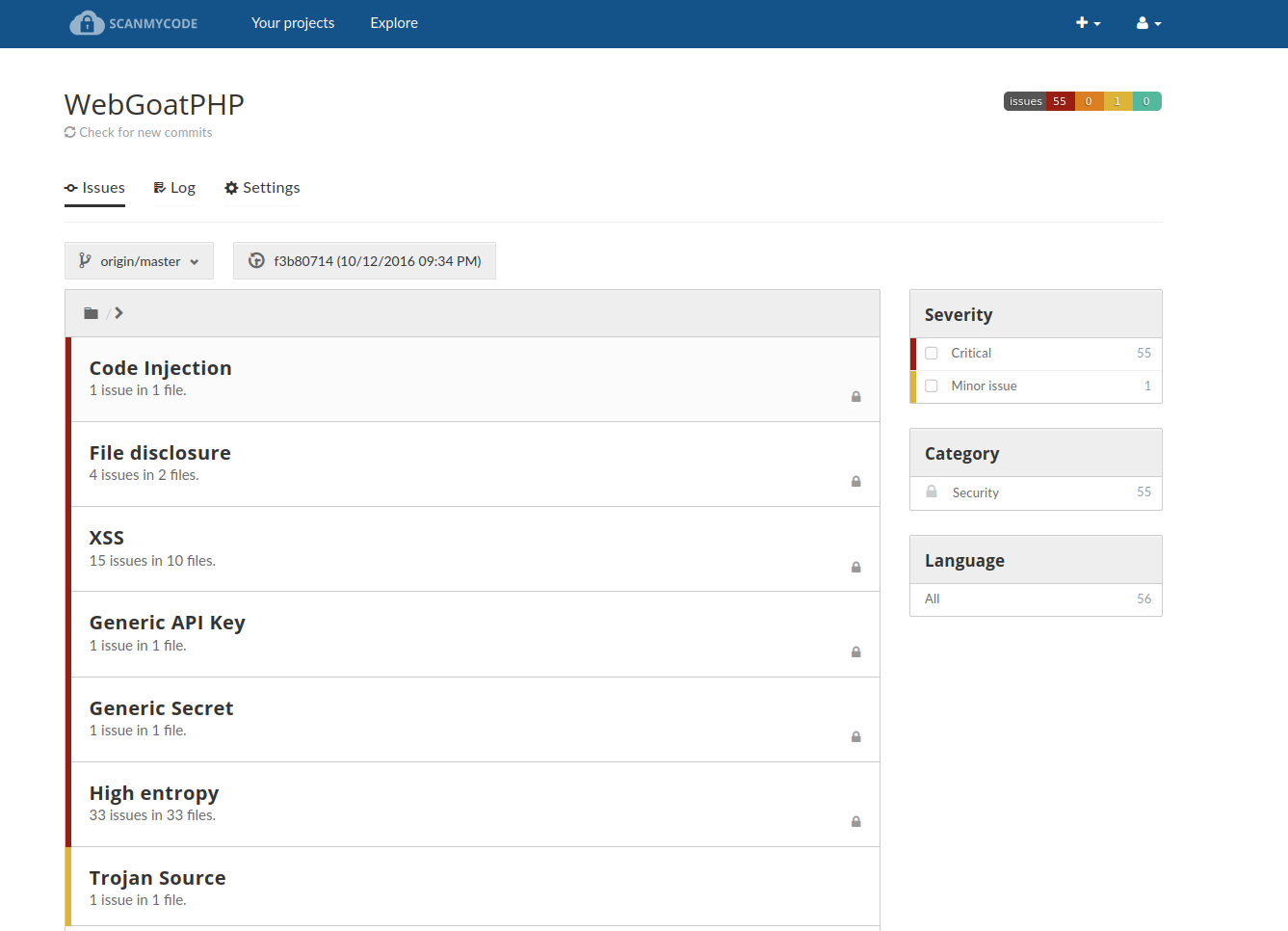
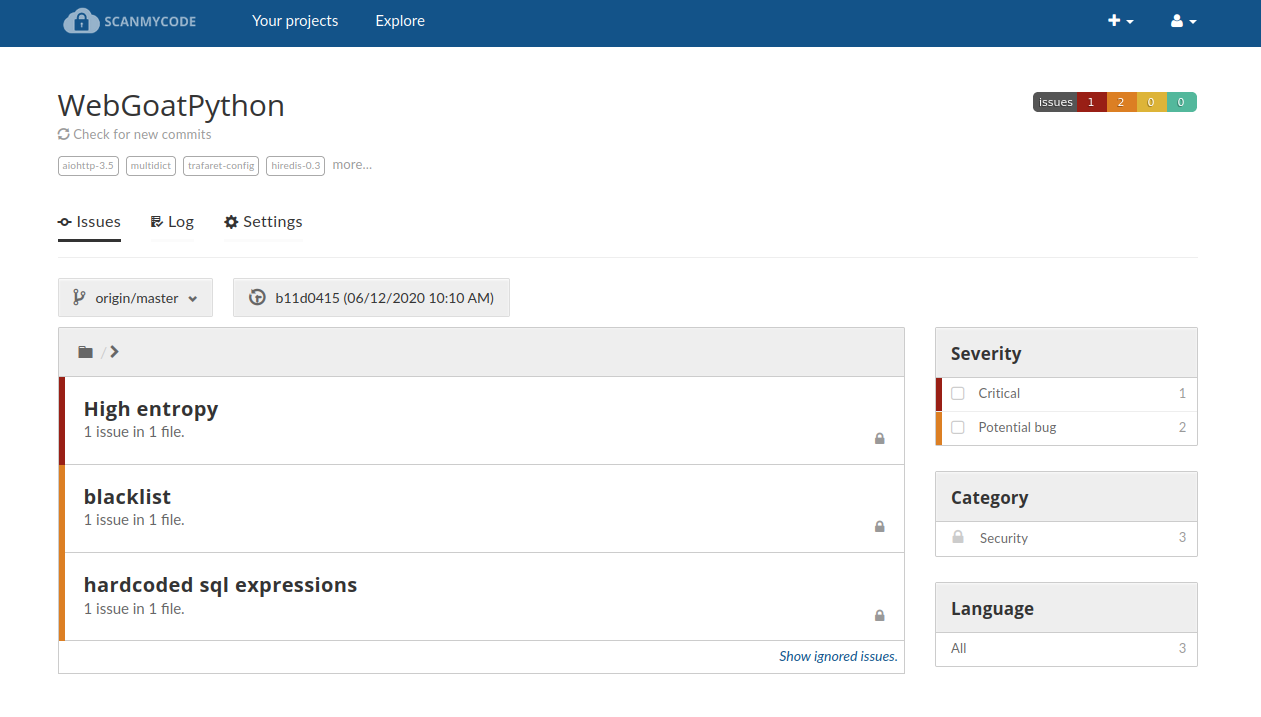
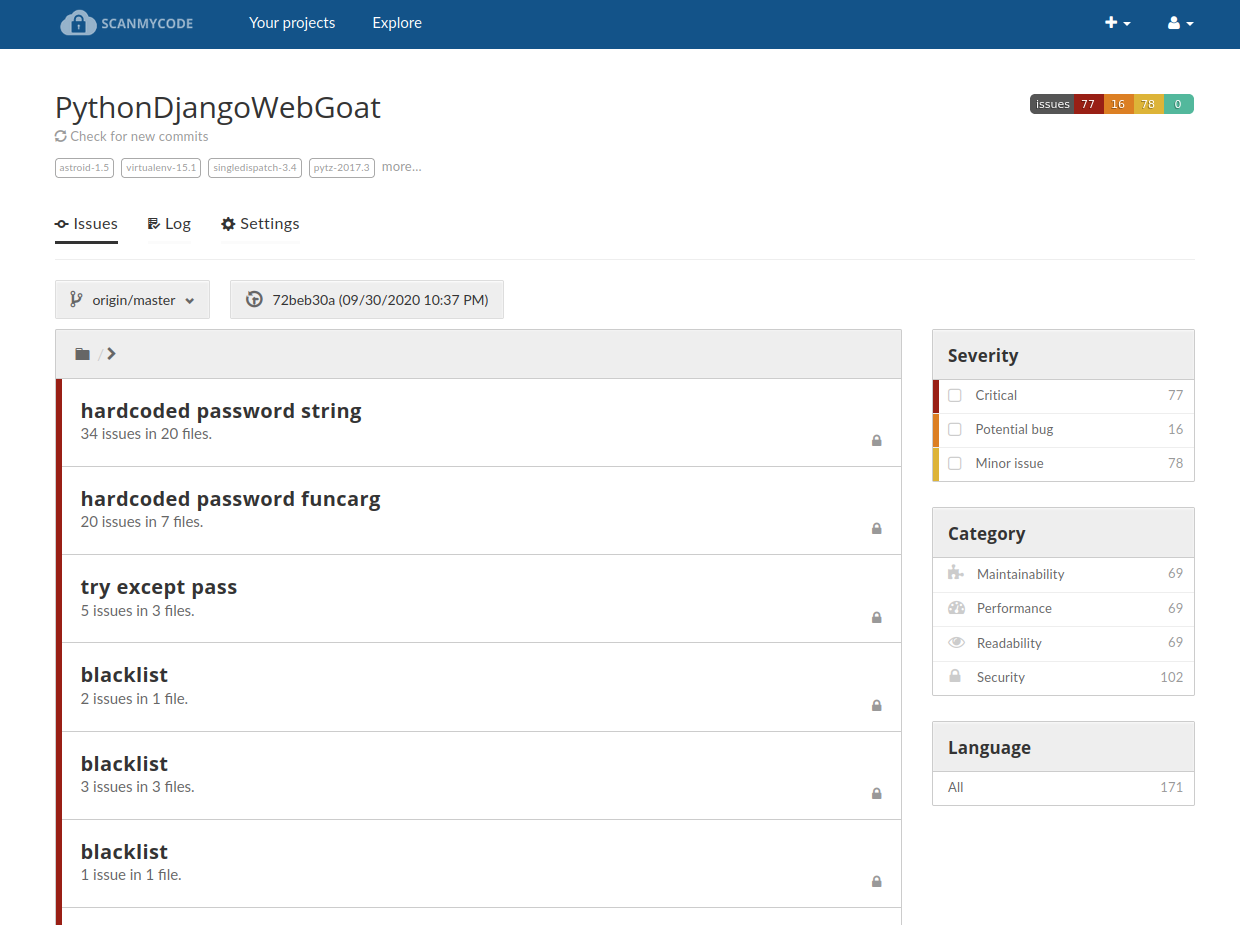
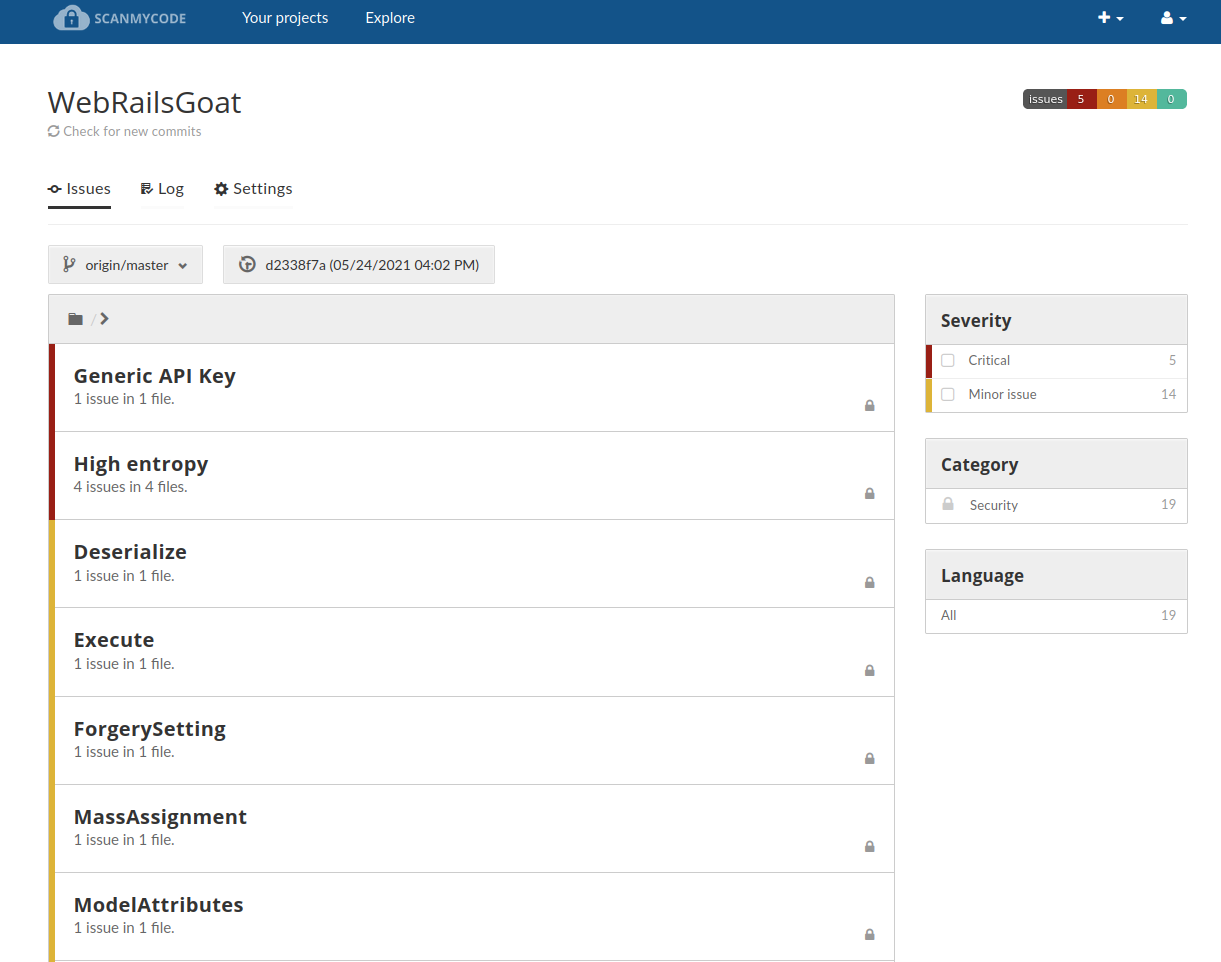
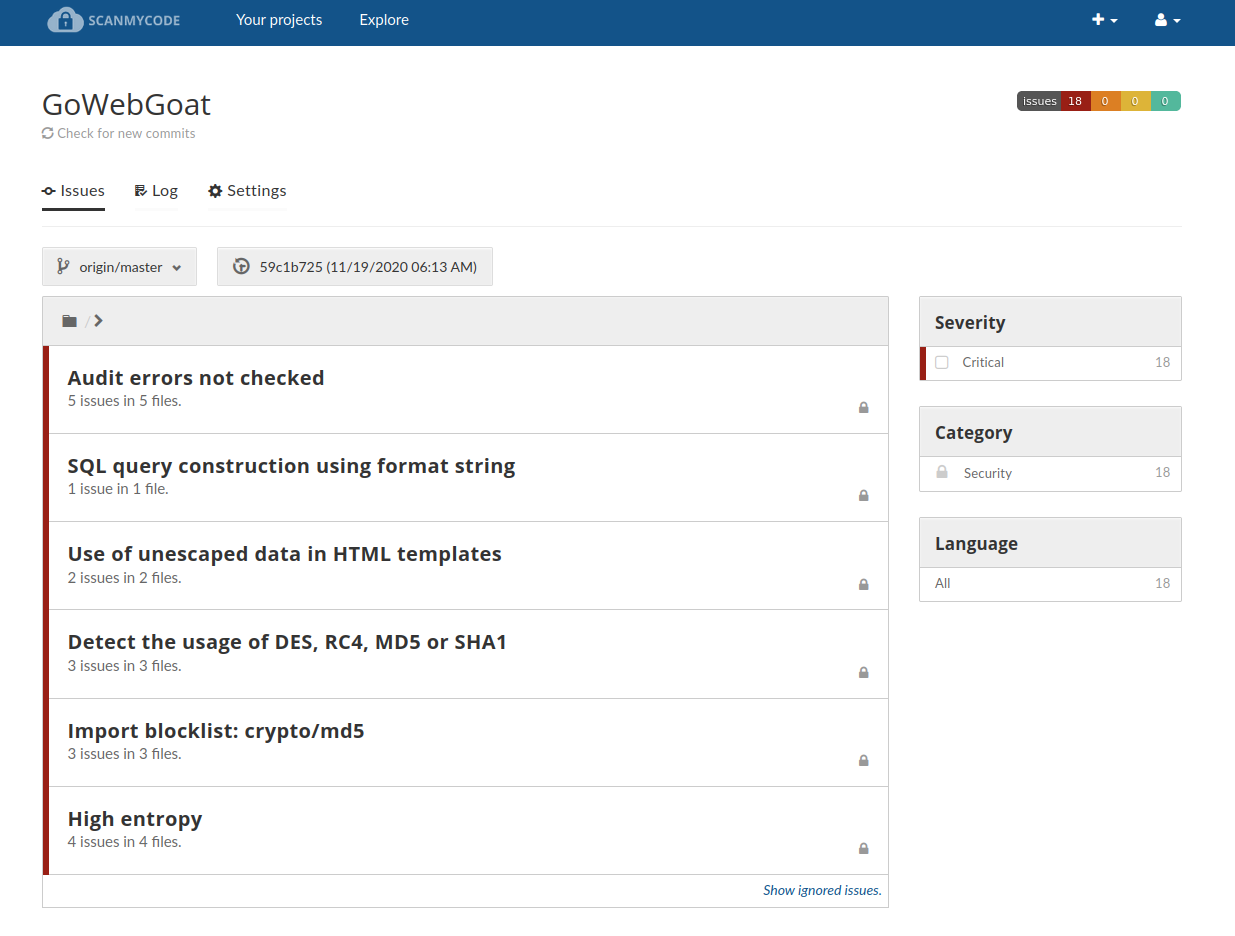
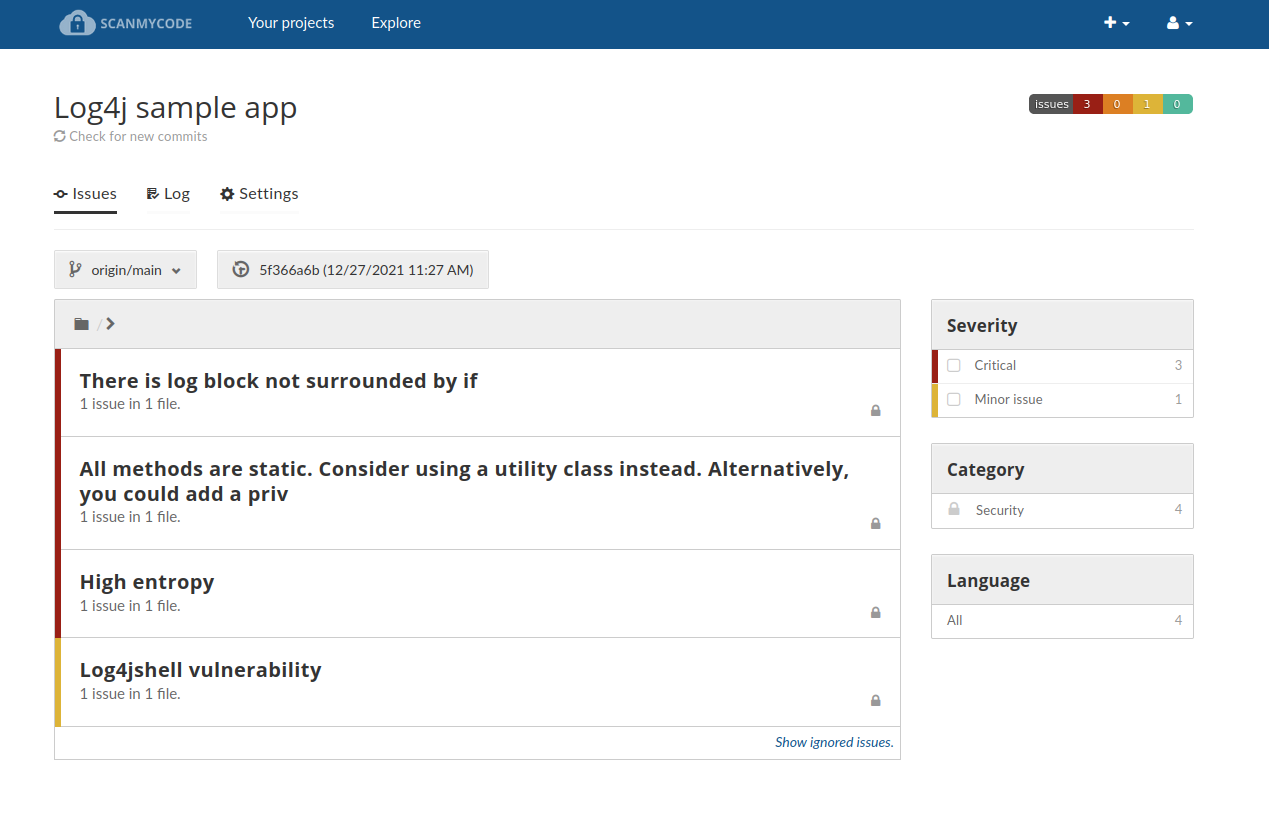
Welcome to Scanmycode CE (Community Edition)!
Scanmycode is based on QuantifedCode. QuantifiedCode is a code analysis & automation platform. It helps you to keep track of issues and metrics in your software projects, and can be easily extended to support new types of analyses. The application consists of several parts:
- A frontend, realized as a React.js app
- A backend, realized as a Flask app, that exposes a REST API consumed by the frontend
- A background worker, realized using Celery, that performs the code analysis
Currently supports: PHP, Java, Scala, Python, Ruby, Javascript, Typescript, GO, Solidity, DeFi Security (DeFi exploits), Secret Scanning, Dependency Confusion, Trojan Source, Open Source and Proprietary Checks (total ca. 1000 checks)
Advantages:
- Many tools, one report (unification)
- Dismiss, collaborate on findings. Mark false-positives
- Enable/disable each individual check in Checkers
- ca. 1000 checks now (Linters, Static Code Analysis/Code Scanning)
- any tool outputting JSON can be added
- fast (checks only new code on recheck)
- Git support (HTTPS/TLS and SSH). For private repositories only SSH.
- all REST API callable (CI/CD integrateable)
- Swiss army knife tool/SIEM for Code Scanning
- 100% Code transparency & full control of your code
Cloud version and more at https://www.scanmycode.today
Cloud version has also many other plugins, also other plugins are commercially available for licensing (GitHub, GitHub organizations, Slack)
See Also: Recon Tool: Findomain
Installation
They provide several options for installing Scanmycode. Which one is the right one for you depends on your use case.
- The manual installation is best if you want to modify or change Scanmycode
- The Docker-based installation is probably the easiest way to try Scanmycode without much work
- The Ansible-based installation is the most suitable way if you want to run Scanmycode in a professional infrastructure (possibly with multiple servers)
The following section will only discuss the manual installation process, for the other options please check their corresponding repositories.
Manual Installation
The installation consists of three parts:
- Install the dependencies required to run Scanmycode
- Download the required source code
- Set up the configuration
Installing Dependencies
Scanmycode requires the following external dependencies:
- A message broker (required for the background tasks message queue). They recommend either RabbitMQ or Redis.
- A database (required for the core application). They recommend PostgreSQL, but SQLite is supported as well. Other database systems might work too (e.g. MySQL), but are currently not officially supported. If you need to run Scanmycode on a non-supported database, get in touch with their team to provide you some guidance.
Download the Scanmycode CE source code
Now with the dependencies installed, you can go ahead and download Scanmycode:
git clone https://github.com/marcinguy/scanmycode-ce.git
Install the required Python packages
Scanmycode CE manages dependencies via the Python package manager, pip.
Edit Settings
Scanmycode gets configured via YAML settings files. When starting up the application, it incrementally loads settings from several files, recursively updating the settings object. First, it will load default settings from quantifiedcode/settings/default.yml. Then, it will check if a QC_SETTINGS environment variable is defined and points to a valid file, and if so it will load settings from it (possibly overwriting default settings). If not, it will look for a settings.yml file in the current working directory and load settings from there. Additionally, it will check if a QC_SECRETS environment variable is defined and points to a valid file, and also load settings from there (this is useful for sensitive settings that should be kept separate from the rest [e.g. to not check them into version control]).
There is a sample settings.yml file in the root of the repository that you can start from.
Running the Setup
After editing your settings, run the setup command via
#run from the root directory of the repository python manage.py setupThe setup assistant will iteratively walk you through the setup, and when finished you should have a working instance of Scanmycode!
Running the web application
To run the web application, simply run
python manage.py runserver
Running the background worker
To run the background worker, simply run
python manage.py runworker
Docker-Based Installation
See docker folder. You can spin up everything using one command.
Ansible-Based Installation
Coming Soon!
See Also: Darkside hacker group, the group that provides ransomware as a service









