Offensive Security Tool: WAF Bypass

Reading Time: 2 Minutes
See Also: A Practical Guide to Hacking Techniques for finding Top Bugs.
The Bug Bounty Hunting Course
Run using Docker
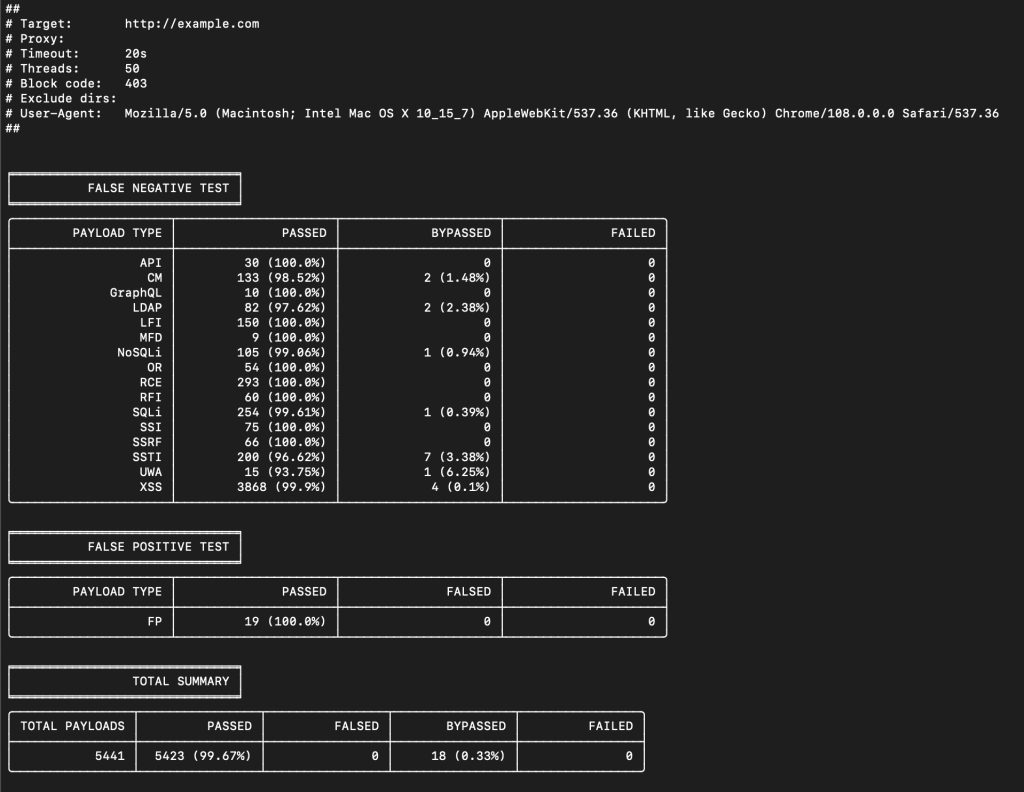
The latest waf-bypass always available via the Docker Hub. It can be easily pulled via the following command:
# docker pull nemesida/waf-bypass## /waf-bypass
Run directly from source code using CLI
# git clone https://github.com/nemesida-waf/waf_bypass.git /opt/waf-bypass/
# python3 -m pip install -r /opt/waf-bypass/requirements.txt# python3 /opt/waf-bypass/main.py --host='example.com'
Options
- ‘–proxy’ (–proxy=’http://proxy.example.com:3128′) – option allows to specify where to connect to instead of the host.
- ‘–header’ (–header ‘Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4=’ –header ‘X-TOKEN: ABCDEF’) – option allows to specify the HTTP header to send with all requests (e.g. for authentication). Multiple use is allowed.
- ‘–user-agent’ (–user-agent ‘MyUserAgent 1/1’) – option allows to specify the HTTP User-Agent to send with all requests, except when the User-Agent is set by the payload (“USER-AGENT”).
- ‘–block-code’ (–block-code=’403′ –block-code=’222′) – option allows you to specify the HTTP status code to expect when the WAF is blocked. (default is 403). Multiple use is allowed.
- ‘–threads’ (–threads=15) – option allows to specify the number of parallel scan threads (default is 10).
- ‘–timeout’ (–timeout=10) – option allows to specify a request processing timeout in sec. (default is 30).
- ‘–exclude-dir’ – exclude the payload’s directory (–exclude-dir=’SQLi,XSS’).
- ‘–json-format’ – an option that allows you to display the result of the work in JSON format (useful for integrating the tool with security platforms). If the option is not specified, the output will be in table format (the default format).
- ‘–details’ – display the False Positive and False Negative payloads. Not compatible with option –json-format option.
- ‘–curl-replay’ – display the cURL command to reproduce False Positive, False Negative or Failed requests. Not compatible with option –json-format option.
See Also: Recon Tool: SauronEye
JSON format
JSON output specification example:
{
"TARGET": "https://example.com", // defined by --host option
"PROXY": {}, // defined by --proxy option
"HEADERS": { // defined by --header option
"User-Agent": ""
},
"BLOCK-CODE": [ // defined by --block-code option
...
],
"THREADS": 50, // defined by --threads option
"TIMEOUT": 30, // defined by --timeout option
"EXCLUDE-DIR": [ // defined by --exclude-dir option
...
],
"FAILED": { // requests with failed processing status
"MFD/7.json": {
"BODY": "WBHTTPSConnectionPool(host='example.com', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=1)"
},
...
},
"PASSED": { // passed requests
"UWA/3.json": {
"URL": "403 RESPONSE CODE"
},
...
},
"FALSED": { // requests with false positive processing status
...
},
"BYPASSED": { // requests with false negative processing status
"UWA/26.json": {
"URL": "200 RESPONSE CODE"
},
...
},
"TestRequest": { // test requests with processing status, exclude passed
"FAILED": {},
"FALSED": {
"UWA/3.json": {
"URL": "403 RESPONSE CODE"
},
...
}
},
"CURL": { // cURL command to reproduce false positive and false negative requests
"FALSED": {},
"BYPASSED": {
"UWA/26.json": {
"URL": "curl -X GET -H 'Accept: */*' -H 'Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate' -H 'Connection: keep-alive' -H 'User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/108.0.0.0 Safari/537.36' 'https://example.com/do.php#.png'"
},
...
}
}
}
Payloads
Depending on the purpose, payloads are located in the appropriate folders:
- FP – False Positive payloads
- API – API testing payloads
- CM – Custom HTTP Method payloads
- GraphQL – GraphQL testing payloads
- LDAP – LDAP Injection payloads
- LFI – Local File Include payloads
- MFD – multipart/form-data payloads
- NoSQLi – NoSQL Injection payloads
- OR – Open Redirect payloads
- RCE – Remote Code Execution payloads
- RFI – Remote File Inclusion payloads
- SQLi – SQL Injection payloads
- SSI – Server-Side Includes payloads
- SSRF – Server-Side Request Forgery payloads
- SSTI – Server-Side Template Injection payloads
- UWA – Unwanted Access payloads
- XSS – Cross-Site Scripting payloads
Write your own payloads
When compiling a payload, the following zones, method and options are used:
- URL – request’s path
- ARGS – request’s query
- BODY – request’s body
- COOKIE – request’s cookie
- USER-AGENT – request’s user-agent
- REFERER – request’s referer
- HEADER – request’s header
- METHOD – request’s method
- BOUNDARY – specifies the contents of the request’s boundary. Applicable only to payloads in the MFD directory.
- ENCODE – specifies the type of payload encoding (Base64, HTML-ENTITY, UTF-16) in addition to the encoding for the payload. Multiple values are indicated with a space (e.g. Base64 UTF-16). Applicable only to for ARGS, BODY, COOKIE and HEADER zone. Not applicable to payloads in API and MFD directories. Not compatible with option JSON.
- JSON – specifies that the request’s body should be in JSON format
- BLOCKED – specifies that the request should be blocked (FN testing) or not (FP)
Except for some cases described below, the zones are independent of each other and are tested separately (those if 2 zones are specified – the script will send 2 requests – alternately checking one and the second zone).
For the zones you can use %RND% suffix, which allows you to generate an arbitrary string of 6 letters and numbers. (e.g.: param%RND=my_payload or param=%RND% OR A%RND%B)
You can create your own payloads, to do this, create your own folder on the ‘/payload/’ folder, or place the payload in an existing one (e.g.: ‘/payload/XSS’). Allowed data format is JSON.
API directory
API testing payloads located in this directory are automatically appended with a header ‘Content-Type: application/json’.
MFD directory
For MFD (multipart/form-data) payloads located in this directory, you must specify the BODY (required) and BOUNDARY (optional). If BOUNDARY is not set, it will be generated automatically (in this case, only the payload must be specified for the BODY, without additional data (‘… Content-Disposition: form-data; …’).
If a BOUNDARY is specified, then the content of the BODY must be formatted in accordance with the RFC, but this allows for multiple payloads in BODY a separated by BOUNDARY.
Other zones are allowed in this directory (e.g.: URL, ARGS etc.). Regardless of the zone, header ‘Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=…’ will be added to all requests.
Disclaimer
It is forbidden to use for illegal and illegal purposes. Don’t break the law. Neither the author nor we are responsible for possible risks associated with the use of this software.
Clone the repo from here: GitHub Link